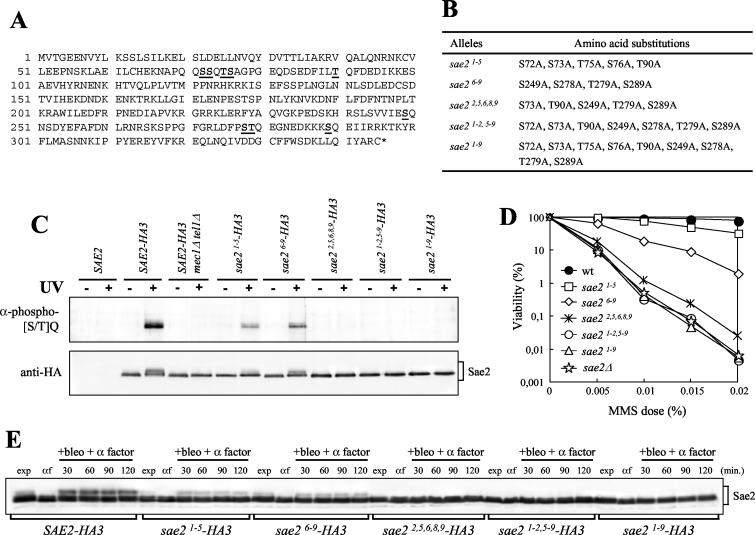
FIG. 6.
Substitutions of S or T to A at putative Sae2 phosphorylation sites affect Sae2 phosphorylation and cell survival after MMS treatment. (A) Sae2 amino acid sequence. Numbers on the left indicate the position of the first amino acid residue in each row. The S or T putative phospho-acceptor residues are boldfaced and underlined. (B) Mutant sae2 alleles obtained by site-directed mutagenesis are listed, together with the resulting serine- or threonine-to-alanine changes. (C) Strains were as follows: SAE2 (YLL1348.1), SAE2-HA3 (YLL1351.8), SAE2-HA3 mec1Δ tel1Δ sml1Δ (DMP3916/5B), sae21-5-HA3 (YLL1359.4), sae26-9-HA3 (YLL1360.31), sae22,5,6,8,9-HA3 (YLL1405), sae21-2,5-9-HA3 (YLL1361.44), and sae21-9-HA3 (YLL1352.2). Immunoprecipitations with anti-HA antibodies were performed on protein extracts prepared from nonirradiated (−) or UV-irradiated (+) α-factor-arrested cells of the indicated genotypes. Immunoprecipitates were subjected to Western blot analysis using polyclonal rabbit anti-phosphorylated-(S/T)Q antibodies (α-phospho-[S/T]Q) and anti-HA antibodies. (D) Dose-response killing curves were determined by plating serial dilutions of wild-type (YLL1348.1), sae2Δ (YLL1069.3), sae21-5 (YLL1353.1), sae26-9 (YLL1354.1), sae22,5,6,8,9 (YLL1395.1), sae21-2,5-9 (YLL1355.1), and sae21-9 (YLL1347.1) cell cultures, growing exponentially in YEPD, onto YEPD plates with or without MMS at the indicated concentrations. Plates were incubated at 26°C, and CFU were counted after 3 days. (E) α-factor-arrested cultures of the strains listed in the legend to panel C were transferred to YEPD medium containing 20 mU of bleomycin/ml and 1 μg of α factor/ml (+bleo + α factor). Time zero (αf) corresponds to cell samples taken immediately before bleomycin addition. Protein extracts prepared from cell samples collected at the indicated times were subjected to Western blot analysis with anti-HA antibodies. exp, exponentially growing cells.