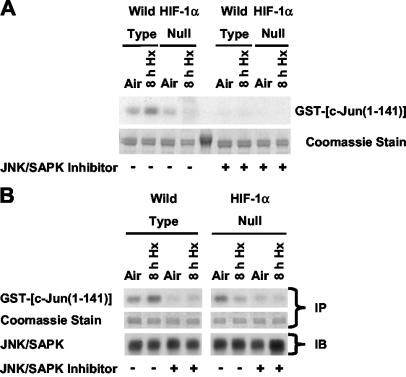
FIG. 2.
HIF-1-dependent JNK activity in cells exposed to hypoxia or anoxia involves JNKs/SAPKs. (A) Autoradiograph of pulldown kinase assays and the corresponding stained gel showing phosphorylation of the GST-c-Jun(1-141) fusion protein substrate extracted from whole-cell lysates of wt and HIF-1α-null mEFs harvested under normoxic conditions (air-5% CO2) or following exposure to hypoxia (pO2, ≤0.01%; 8 h). Beads with adsorbed fusion protein were thoroughly washed, and then kinase assays were performed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of a peptide JNK/SAPK inhibitor (1.7 μM). For details, see Materials and Methods. (B) (Top) Representative autoradiographs showing phosphorylation of the GST-c-Jun(1-141) fusion protein substrate by JNKs/SAPKs immunoprecipitated from whole-cell lysates of wt and HIF-1α-null mEFs harvested under normoxic conditions (air-5% CO2) or following exposure to hypoxia (pO2, ≤0.01%; 8 h). Kinase assays were performed in the absence (−) or presence (+) of the peptide JNK/SAPK inhibitor (1.7 μM). (Center) Corresponding stained gels for the immunoprecipitation assays (immunocomplex kinase assays) shown above. (Bottom) Immunoblots of total JNKs/SAPKs immunoprecipitated from the same whole-cell lysates of wt and HIF-1α-null mEFs used for the immunocomplex kinase assays shown above. Blots were probed with a primary anti-JNK2 monoclonal antibody (cross-reactive with mouse JNK1 and JNK3) and a secondary anti-mouse IgG antibody conjugated with horseradish peroxidase. IP, immunoprecipitation assay; IB, immunoblot assay.