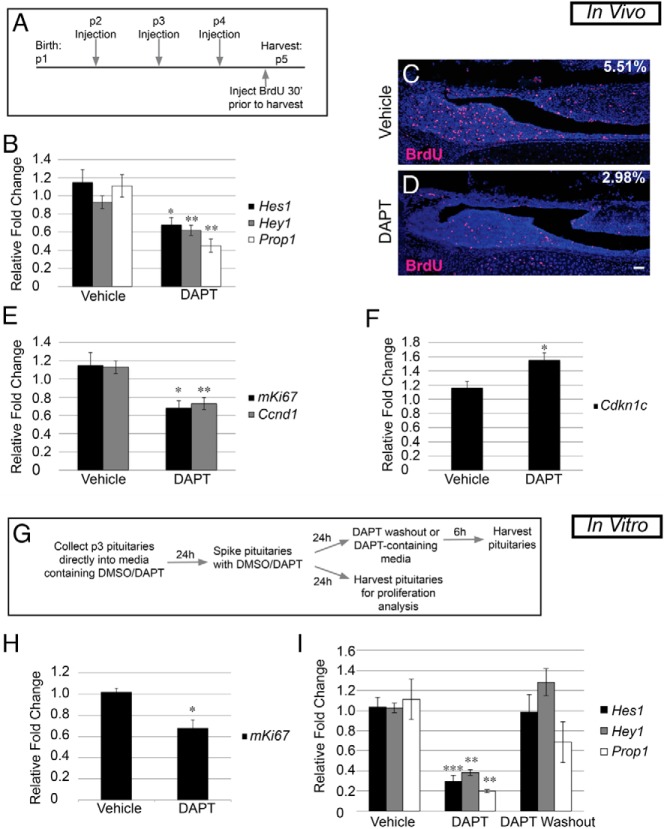
Figure 5.
Postnatal Notch inhibition results in decreased proliferation and identifies Prop1 as a direct target. A, Experimental design for in vivo DAPT injection. B, Subcutaneous injection with DAPT results in a decrease in whole pituitary mRNA levels of Hes1, Hey1, and Prop1 compared with those in vehicle-injected mouse pituitaries. C and D, BrdU-positive cells (red) are present throughout the pituitaries of vehicle-treated mice (C, 5.51 ± 0.20%) and are significantly reduced (P = .0001) in pituitaries of DAPT-treated mice (D, 2.98 ± 0.26%). E, mRNA levels of mKi67 and Ccnd1 in whole pituitaries are decreased after DAPT injection compared with those after for vehicle injection. F, Conversely, mRNA levels of Cdkn1c are increased in the whole pituitary of DAPT-injected mice. G, Experimental design for in vitro DAPT treatment and DAPT washout assay. H, After 48 hours in culture, mRNA levels of mKi67 are significantly decreased compared with those of vehicle-treated controls. I, mRNA levels of Hes1, Hey1, and Prop1 are reduced after DAPT treatment and recover after 6 hours of DAPT washout. Magnification, ×100. Bars, 50 μm. *, P < .05; **, P < .01; ***, P < .001. n = 4 (immunohistochemistry), n = 5 to 8 (qRT-PCR in vivo), and n = 4 to 8 (qRT-PCR in vitro).