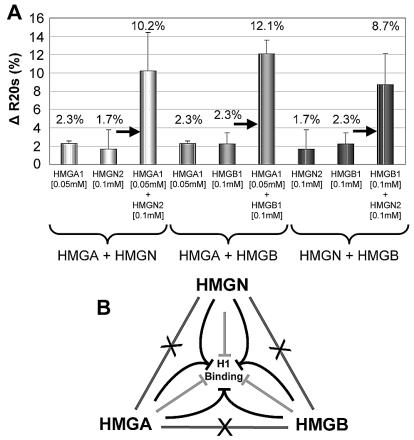
FIG. 5.
HMG proteins act synergistically to compete with H1 for chromatin binding. (A) Shown are the ΔR20s values between uninjected and injected cells expressing H1°-GFP (see Fig. 2D). The concentration of the injected proteins is indicated below each bar. (B) Scheme of the H1-HMG chromatin binding network. The lines connecting the HMG families, crossed by an X, indicate lack of competition between members of different HMG families. The light gray lines indicate that, by itself, each of the HMG families reduces the binding of H1 to chromatin. The converging black lines indicate that members of distinct HMG families weaken the binding of H1 to chromatin synergistically. The scheme points emphasize that H1 is a target common to all of the HMG proteins.