Figure 3.
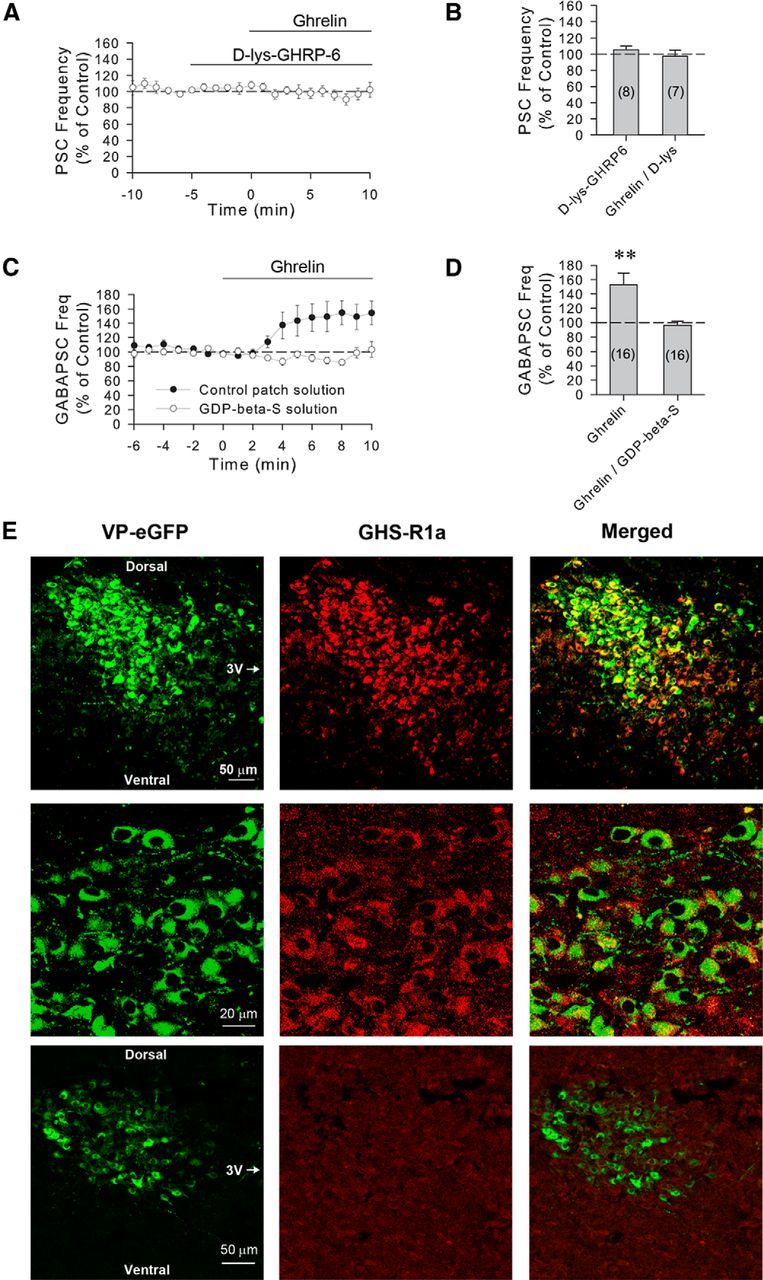
The ghrelin modulation of GABA synaptic inputs to VP neurons is mediated by postsynaptic ghrelin receptors. A, Time course of mean normalized frequency of sPSC frequencies, as a percentage of baseline, showing that the increase in sPSC frequency caused by ghrelin (100 nm) is blocked by the ghrelin GHS-1a receptor antagonist d-lys-GHRP-6 in VP neurons from 24 h-fasted rats (n = 8). B, Summary of effect of d-lys-GHRP-6 and d-lys-GHRP-6 plus ghrelin application on the mean sPSC frequency, as a percentage of baseline. C, Time course of mean normalized GABAergic sPSC frequencies in PVN VP neurons from fasted rats with and without G-protein blockade. Intracellular application of the G-protein blocker GDP-β-S (1 mm) via the patch electrode solution (n = 16) blocked the ghrelin-induced increase in GABAergic sPSC frequency seen in control recordings (n = 16), indicating a postsynaptic G-protein-dependent mechanism that mediates the ghrelin effect in VP cells. D, Summary of mean normalized GABAergic sPSC frequencies, as a percentage of baseline, with and without postsynaptic G-protein blockade. Blocking postsynaptic G-protein activity with intracellular GDP-β-S application blocked the ghrelin-induced increase in GABAergic sPSCs in VP neurons. E, Confocal micrographs of a section of the PVN showing eGFP-labeled VP neurons under green emission filters (VP-eGFP) and GHS-R1a-immunolabeled neurons under red emission filters (GHS-R1a), and the overlay (Merged) of the two images showing eGFP-GHS-R1a double labeling at low (top row) and high magnifications (middle row). Bottom row, Preabsorption control, showing a low-magnification confocal micrograph of a section of the PVN in which the primary antibody had been preabsorbed with a synthetic GHS-R1a peptide. Dorsal, ventral, and medial (third ventricle [3V]) aspects are indicated for orientation. **p < 0.01.
