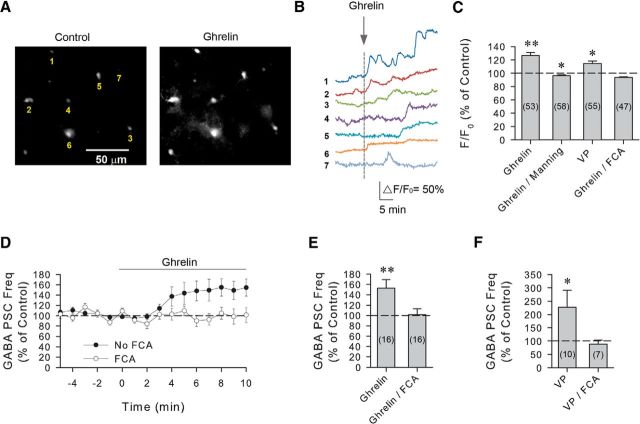
Figure 5.
The ghrelin-induced increase in synaptic GABA inputs to VP neurons is mediated by astrocytes. A, Standard fluorescence images of a Rhod-2 AM-loaded slice of PVN from a 24 h-fasted rat showing calcium levels in astrocytes before (Control) and after the bath application of ghrelin (Ghrelin, 100 nm). B, Calcium measurements of the ghrelin-induced increases in calcium levels in the 7 glial cells (1–7) labeled with Rhod-2 AM in the PVN brain slice shown in A. C, Summary of mean normalized fluorescence in PVN astrocytes. Bath application of ghrelin caused a significant increase in intracellular calcium (Ghrelin); the ghrelin response was blocked with the V1a receptor antagonist Manning compound (Ghrelin/Manning); bath application of VP also caused a significant increase in intracellular calcium (VP) in Rhod-2 AM-loaded cells; preincubation of the slices in the gliotoxin FCA blocked the ghrelin-induced increase in astrocytic calcium (Ghrelin/FCA). D, Time course of the mean normalized GABAergic sPSC frequency response to ghrelin in the presence and absence of FCA in PVN VP neurons from 24 h-fasted rats. Pretreatment of PVN brain slices with FCA blocked the ghrelin-induced increase in GABAergic PSC frequency (n = 16). E, Summary of the mean normalized GABAergic sPSC frequency response to ghrelin in VP neurons in the absence (Ghrelin) and presence of FCA (Ghrelin/FCA). F, Summary of the mean normalized GABAergic sPSC frequency response to VP in VP neurons in the absence (VP) and presence of FCA (VP/FCA). FCA blocked the VP-induced increase in GABAergic PSC frequency in VP neurons. *p < 0.05. **p < 0.01.