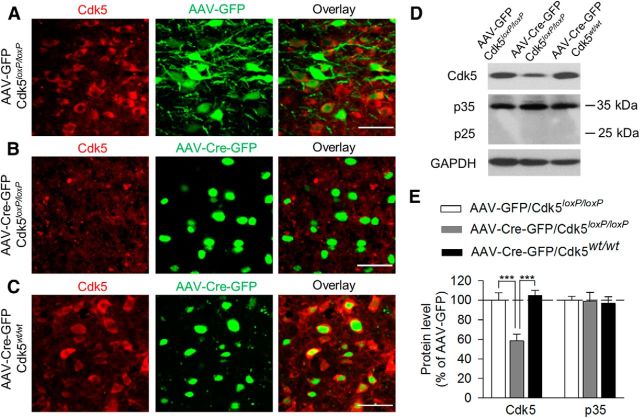
Figure 3.
AAV2-Cre-GFP-mediated VTA-specific deletion of Cdk5 in the VTA. After the behavioral tests, Cdk5 protein levels in the VTA were determined using immunofluorescence labeling (A–C) and Western blotting (D,E). Timeline for the AAV microinjection, behavioral tests, immunofluorescence labeling, and Western blotting is shown in Figure 2A. A–C, Immunofluorescence labeling showed that Cdk5 was expressed in the VTA in Cdk5loxP/loxP mice that received intra-VTA injection of AAV2-GFP (A) or in Cdk5wt/wt mice that received intra-VTA injection of AAV2-Cre-GFP (C). However, Cdk5 was lost in the VTA in Cdk5loxP/loxP mice that received intra-VTA injection of AAV2-Cre-GFP (B). Scale bar, 50 μm. D, E, Representative (D) and summarized (E) data of Western blots for Cdk5, p35/25, and GAPDH showing that VTA-specific deletion of Cdk5 significantly decreased protein levels of Cdk5 in the VTA (p < 0.001) without affecting the protein levels of Cdk5 cofactor p35 (p > 0.05). Immunoreactivity was normalized to GAPDH and is presented as a percentage of that of Cdk5loxP/loxP mice with AAV2-GFP injection group. The p values for Tukey's post hoc test results are shown on the top (***p < 0.001; n = 6 mice/group).