Figure 6.
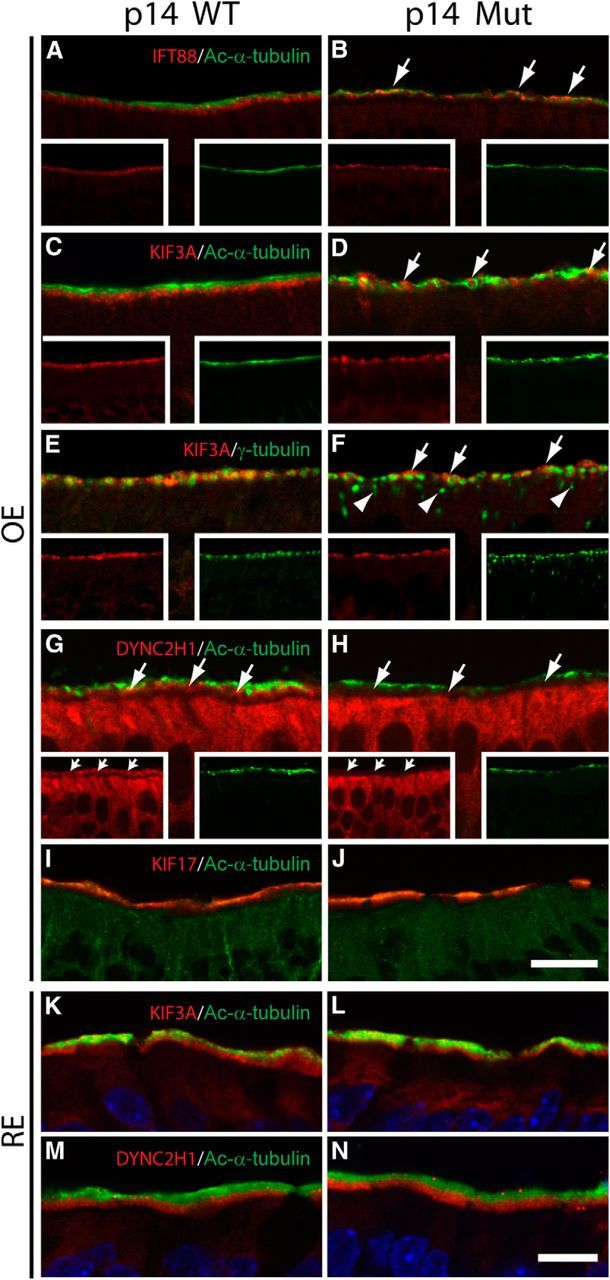
Mislocalized IFT components in P14 Cetn2 mutant OE. A, B, IFT88 (red) and Ac-α-tubulin (green) colabeling of WT (A) and mutant (B) OE where IFT88 is localized in the ciliary layer (arrows) of the mutant. C, D, KIF3A (red) and Ac-α-tubulin (green) colabeling of WT (C) and mutant (D) OE. KIF3A signal (arrows) appears intermingled with that of Ac-α-tubulin (green) in the mutant ciliary layer. E, F, KIF3A (red) and γ-tubulin (green) colabeling of WT (E) and mutant (F) OE. Note KIF3A localization (arrows) above the most superficial γ-tubulin signal in mutant. Arrowheads (F, mutant) indicate mislocalized basal bodies. G, H, DYNC2H1 (red) and Ac-α-tubulin (green) colabeling of WT (G) and mutant (H) OE. DYNC2H1 labels WT knob layer, and is reduced dramatically in the mutant (arrows). Note that DYNC2H1 labeling of mutant dendrite and soma layer is unaltered. Insets in A–H are single channel images of each labeling. I, J, KIF17 (red) and Ac-α-tubulin (green) colabeling of WT (I) and mutant (J) OE, showing KIF17 localization in cilia layer of both. K, L, KIF3A (red) and Ac-α-tubulin (green) colabeling of P14 nasal respiratory epithelium. KIF3A appears concentrated at the ciliary bases of both WT (K) and mutant (L). M, N, DYNC2H1 (red) and Ac-α-tubulin (green) colabeling of P14 nasal respiratory epithelium, showing cytoplasmic dynein 2 concentration at ciliary bases of both WT (M) and mutant (N). Scale bars: A, B, I, J, 30 μm; C–H, 20 μm; K–N, 50 μm.
