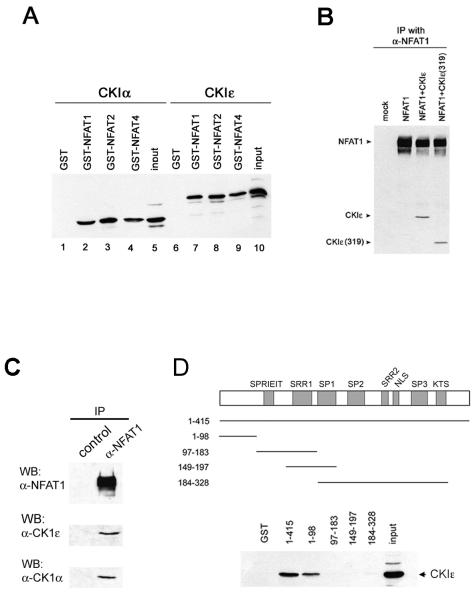
FIG. 3.
Interaction of NFAT family members with CK1. (A) GST fusion proteins containing the regulatory domains of NFAT proteins bind CK1 isoforms. GST or GST fusion proteins encompassing the regulatory domains of NFAT1, NFAT2, or NFAT4 were incubated with HEK 293 cell lysates that were either mock transfected or transfected with CK1 isoform α or ɛ. Bound proteins were visualized by Western blotting and sequential probing with antibodies against CK1α and CK1ɛ. (B) NFAT1 interacts with the kinase domain of CK1. Full-length HA-tagged NFAT1 was expressed in HEK 293 cells either alone, in combination with HA-tagged full-length CK1ɛ, or in combination with C-terminally truncated CK1ɛ [CK1ɛ(319)]. NFAT1 was immunoprecipitated with an anti-NFAT1 antibody, and precipitated proteins were visualized by Western blotting with an antibody against the HA tag. (C) Endogenous NFAT1 and CK1 stably associate. NFAT1 was immunoprecipitated from Jurkat T cells with either an anti-NFAT1 antibody or preimmune serum. The presence of associated CK1 in the immunoprecipitates was detected by Western blotting (WB) with antibodies against CK1α or CK1ɛ. (D) The region of NFAT1 that mediates CK1 binding maps to the N-terminal transactivation domain. GST fusion proteins encompassing various regions of the NFAT1 regulatory domain were incubated with cell lysates transfected with CK1ɛ. Fusion proteins able to associate with CK1 were detected by Western blot analysis using anti-CK1ɛ.