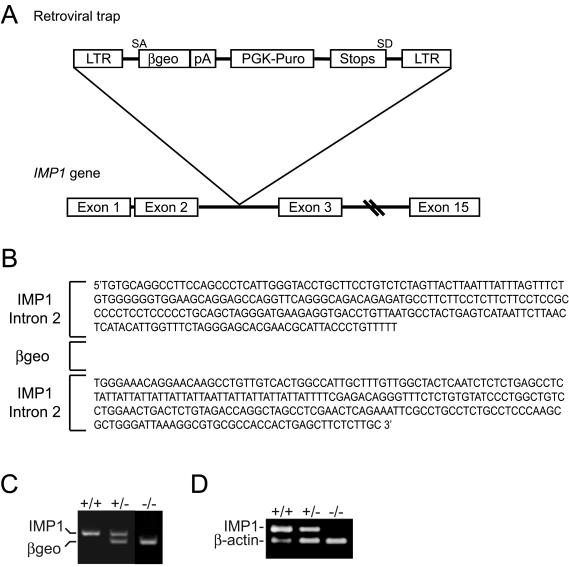
FIG. 1.
Generation of IMP1-deficient mice. (A) Schematic representation of the insertion of the retroviral gene trap vector into intron 2 of the Imp1 gene. Exons are represented as boxes. LTR, long terminal repeat; β-geo, β-galactosidase-neomycin resistance cassette; PGK, phosphoglycerate kinase 1; Puro, puromycin; SA and SD, splice acceptor and splice donor sites, respectively. (B) Imp1 intron 2 sequences flanking the retroviral insert. Splicing of the gene trap produces a transcript containing an IMP1-β-geo fusion molecule that includes the first of the two RRM modules encoded by exons 1 and 2 but lacks the second RRM motif and the remaining four KH domains, which are encoded by exons 3 to 15. (C) Genotyping of wild-type, Imp1+/−, and Imp1−/− mice by multiplex RT-PCR. The reaction resulted in a 396-bp wild-type fragment and the 298-bp β-geo fragment with Imp1- and β-geo-specific primers and genomic DNA from mouse tails. The products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by ethidium bromide staining. (D) Expression of the Imp1 transcript in wild-type, Imp1+/−, and Imp1−/− mice. RNA from E12.5 embryos were examined for Imp1 expression by multiplex RT-PCR with specific primers for Imp1 and β-actin, resulting in 237-bp and 157-bp PCR fragments, respectively. The products were separated by agarose gel electrophoresis and visualized by ethidium bromide staining.