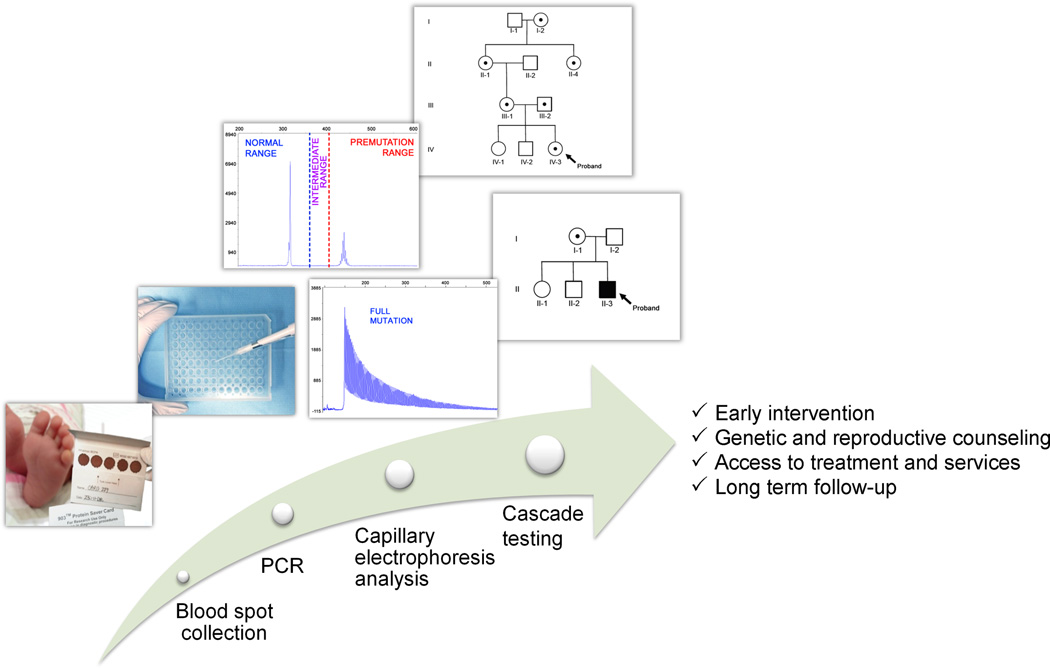
Figure 1.
Diagram of the newborn-screening process. From the left, blood collected on a bloodspot card from a heel prick is used to screen newborns for Fragile X. Isolation of DNA, PCR and Capillary Electrophoresis analysis allow measurement of CGG-repeat allele size. The identification of individuals with an FMR1 expanded allele can lead to cascade testing of extended family members. The benefits of cascade testing include early intervention, genetic and reproductive counseling, access to behavioral and pharmacological treatment, and long-term follow-up services.