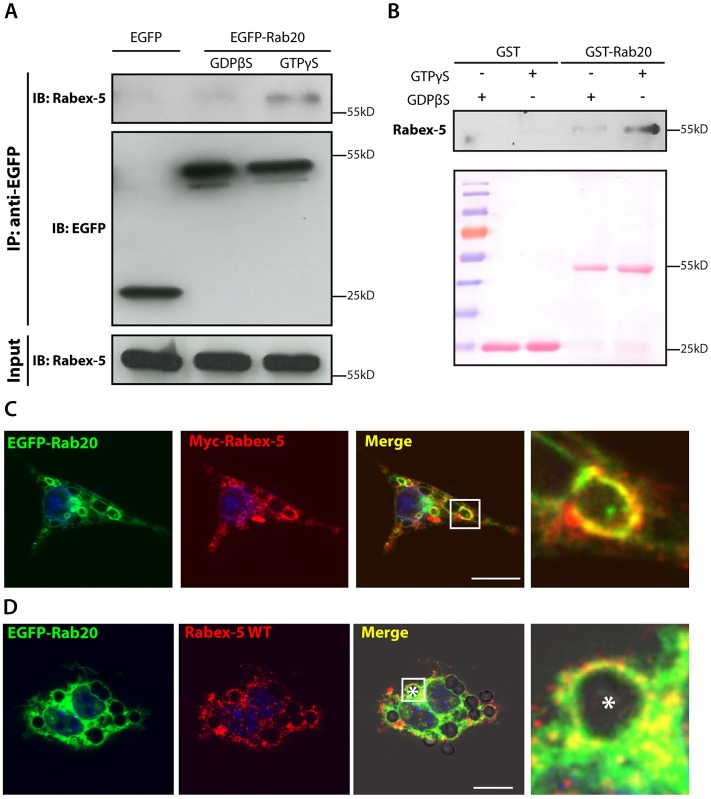
Fig. 6.
Rabex-5 is an effector of Rab20. (A) Co-immunoprecipitation of Rabex-5 from EGFP–Rab20-expressing macrophages. Macrophages stably expressing EGFP–Rab20 were lysed in buffer supplemented with either GTPγS or GDPβS and incubated with GFP–Trap® beads. Lysates were analyzed by SDS-PAGE, and EGFP and Rabex-5 were detected by western blotting. (B) The in vitro interaction of Rabex-5 and GTP–Rab20. GST or GST–Rab20 were immobilized on agarose beads, preloaded with either GTPγS or GDPβS and incubated with a lysate from RAW264.7 macrophages. After washing, the beads were collected, analyzed by SDS-PAGE and Rabex-5 was detected by western blotting. Ponceau S staining (lower panel) shows protein loading. (C) Colocalization of EGFP–Rab20 and wild-type (WT) Myc–Rabex-5 in macrophages. RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with EGFP–Rab20 and wild-type Myc–Rabex-5 and subsequently fixed. (D) Colocalization of EGFP–Rab20 and wild-type Myc–Rabex-5 on phagosomes. RAW264.7 macrophages were transfected with EGFP–Rab20 and wild-type Myc–Rabex-5 and subsequently incubated with 3-µm IgG-coated beads. Nuclei were stained with Hoechst 33258 and are shown in blue. Magnified images show the regions of interest (indicated by white squares in the lower-magnification images). White asterisk, the phagosome. Scale bars: 10 µm.