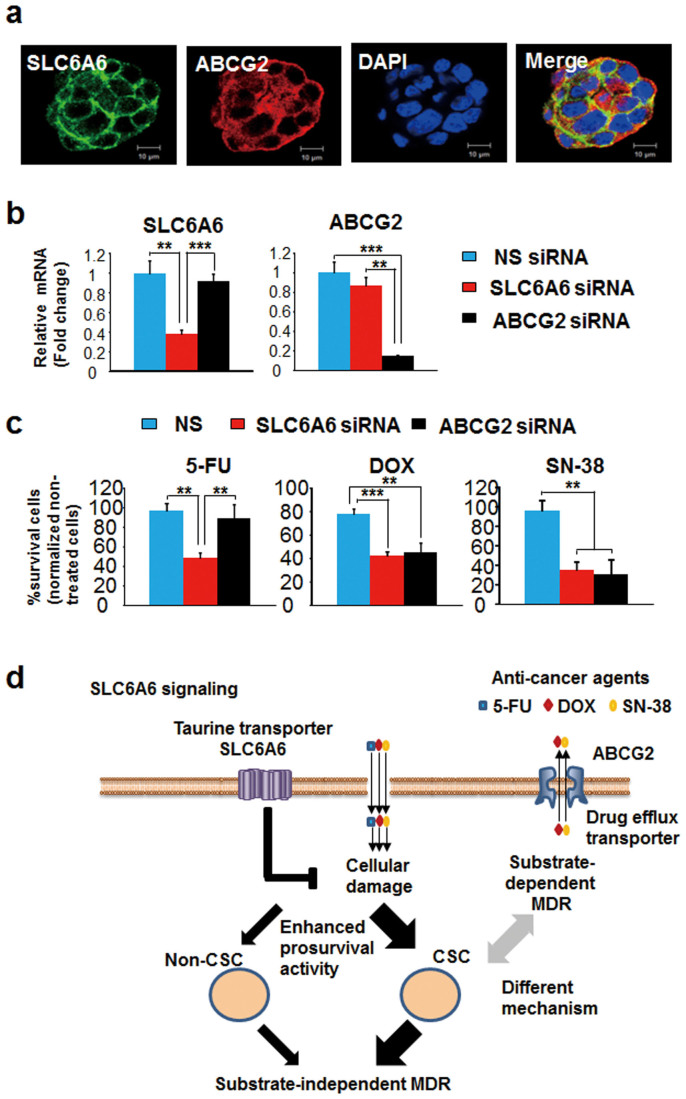
Figure 6. The MDR phenotype and mechanism of taurine-SLC6A6 signalling are different from those of the ABCG2 ABC transporter.
(a) SLC6A6 (green), ABCG2 (red) and nuclear (blue) immunostaining of HCT-15 cells. Bar: 10 μm. (b) Quantitative RT-PCR of SLC6A6 and ABCG2 in cells treated with nonspecific control-, SLC6A6- or ABCG2-siRNA. NS, nonspecific control. Each bar represents n = 3; means ± SD. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (Student's t-test). (c) Drug resistance activity of cells treated with nonspecific control-, SLC6A6- or ABCG2-siRNA. The cells were treated with 3 μM 5-FU, 0.1 μM doxorubicin (DOX) or 0.01 μM SN-38 for 72 h. The percentage of surviving cells was calculated as the ratio of treated to untreated cells. Each bar represents n = 3; means ± SD. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 (Student's t-test). (d) Schema of model. SLC6A6, which is overexpressed in CRC cells, enhances the prosurvival activity of CRC cells, particularly in highly chemoresistant cancer stem cells (CSCs), thereby promoting multidrug resistance (MDR). This mechanism is quite different from that of the ABCG2-dependent drug-efflux machinery pathway.