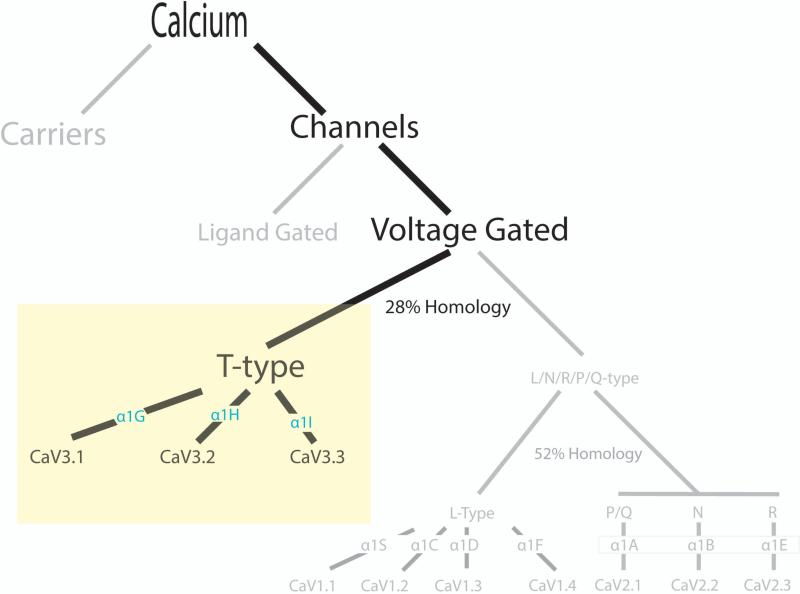
Figure 1. Calcium Homeostasis through T-type Calcium Channels.
Calcium can enter a cell through either calcium carriers or calcium channels. Calcium channels can be further subdivided into ligand gated or voltage gated. Voltage gated calcium channels can be characterized by high voltage (CaV1 L-type and CaV2 N, P/Q, and R-types) or low voltage (T-type). L, N, P/Q, R-types and T-type calcium channels are further characterized by their alpha subunits into CaV1.1 (α1S), 1.2 (α1C), 1.3 (α1D), 1.4 (α1F), CaV 2.1 (α1A), 2.2 (α1B), 2.3 (α1E), and CaV3.1 (α1G), 3.2 (α1H), 3.3 (α1I). The degrees of homology between classes are noted.