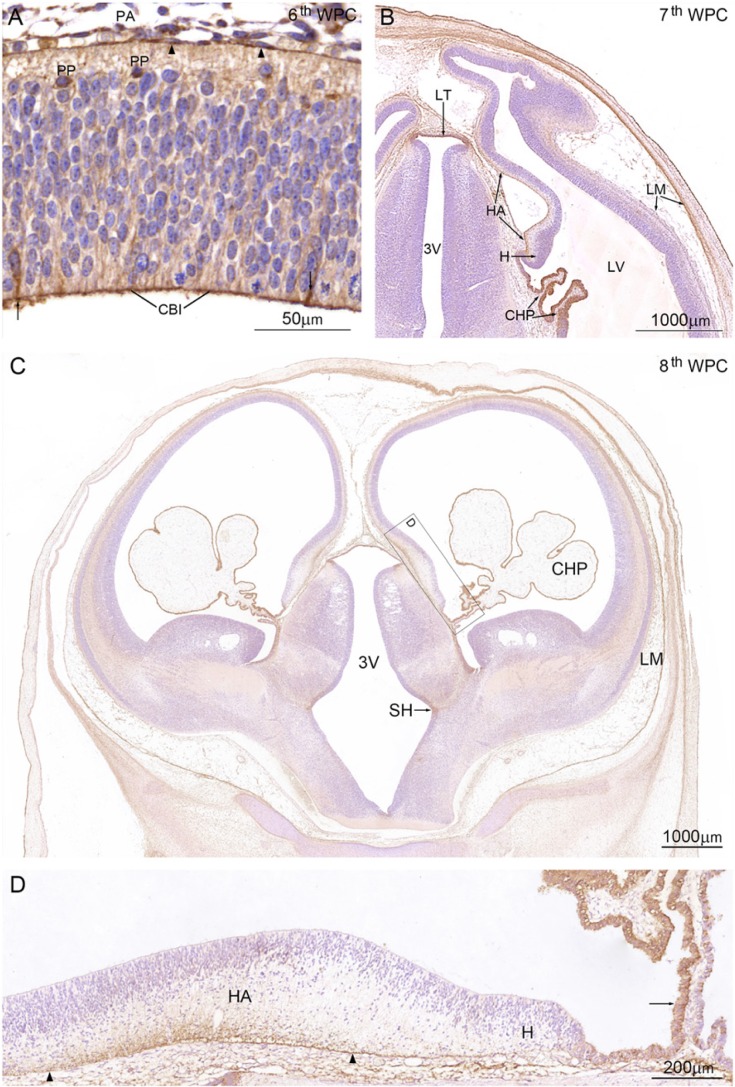
Figure 2.
YKL-40 protein distribution in a coronal section from an embryo at the 6th wpc (crown-rump length (CRL): 7 mm). (A) Leptomeningeal cells (arrowheads) in the pia-arachnoid (PA) have strong YKL-40 immunoreactivity. Apical surfaces of neuroepithelial cells forming the CSF-brain interface (CBI) are outlined by YKL-40 immunoreactivity and some neuroepithelial cells/radial glial cells (arrows) and preplate cells (PP) are YKL-40 positive. (B) Coronal section from a 7th wpc human embryo (CRL: 20 mm). The YKL-40 positive outer surface of the hippocampal anlage (HA) is shown between the two arrows. Epithelial cells of the newly-formed lateral ventricular choroid plexus (CHP) have strong YKL-40 immunoreactivity. The cortico-choroid boundary between the hem (H) and the plexus is YKL-40 positive. Leptomeninges (LM), in particular, the continuous part of the arachnoid, show strong YKL-40 immunoreactivity. In the rostral part of third ventricle (3V) the lamina terminalis (LT) shows strong YKL-40 immunoreactivity. (C) Coronal section from a late 8th wpc human embryo (CRL: 31 mm). Note the distinct reactivity of the LM and CHP epithelium compared with that of the telencephalic wall, where only marginal and intermediate zones show a weak YKL-40 immunoreactivity. A prominent sulcus hypothalamicus (SH) is seen in 3V. The boxed area includes the hippocampal anlage (HA), the hem (H) and the root of the choroid plexus, and is shown in higher magnification in (D). End feet and the outer marginal zone of the developing CA1 to CA4 of the hippocampus (between the arrowheads) show strong YKL-40 immunoreactivity. The dentate primordium between the right arrowhead and the hem is only immunostained in the end feet region in contrast to the unstained hem, which extends to the choroid plexus where the part of the root (arrow) adjacent to the hem shows strong YKL-40 immunoreactivity. Scale bars: A: 50 μm; B-C: 1000 μm; D: 200 μm.