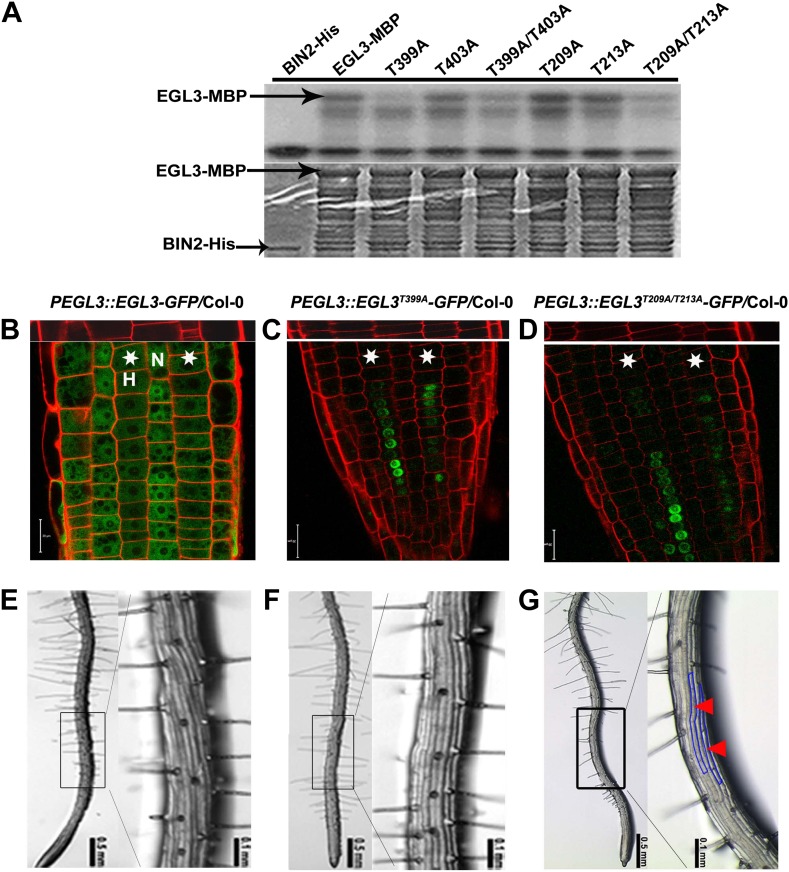
Figure 6. BIN2 phosphorylates EGL3 to regulate its subcellular localization and root epidermal cell fate.
(A) BIN2 phosphorylates EGL3 on T399 and T209/T213. An equal amount of recombinant protein, as indicated by Coomassie brilliant blue (CBB) staining (bottom panel), was incubated in phosphorylation buffer, separated by SDS–PAGE, and followed by autoradiography (top panel). (B) EGL3-GFP is predominantly localized in N cell nuclei. Both EGL3T399A-GFP (C) and EGL3T209A/T213A-GFP (D) are solely localized in H cell nuclei. For (B–D), the 5-day-old roots were stained with propidium iodide (red) for 10 s for visualizing the cell wall. The top panels show the underlying cortex. The stars indicate H cells. Scale bars, 20 μm. (E–G) Root hair patterns of EGL3-GFP (E), EGL3T399A-GFP (F), and EGL3T209A/T213A-GFP (G) transgenic plants. Outlined areas in the left images are magnified in the right images. Red arrowheads and areas outlined with blue lines indicate ectopic non-root hair cells in the H position.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.02525.012