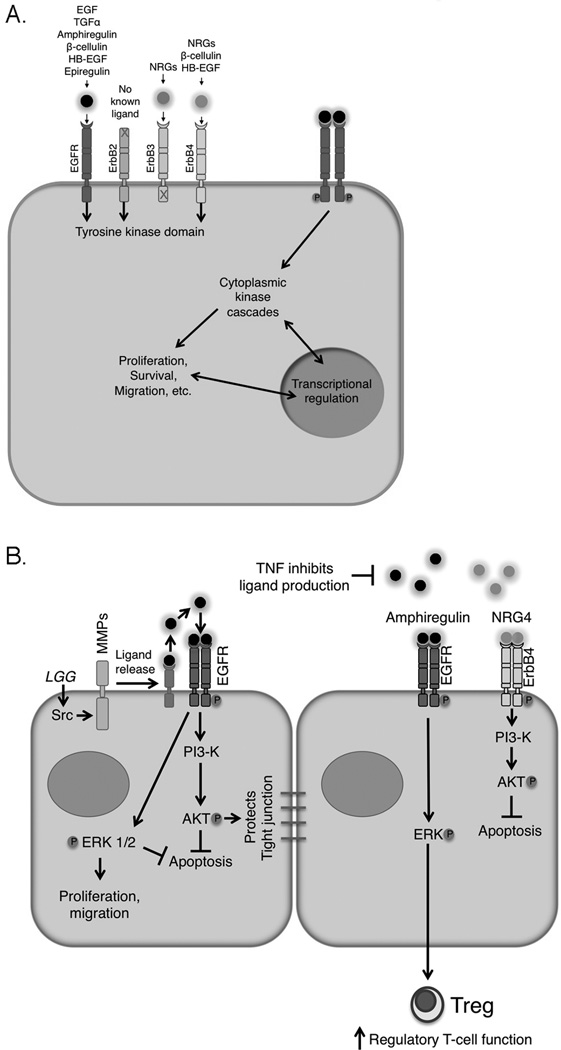
Figure 1.
ErbB receptors and their ligands play key roles in intestinal epithelial integrity. (A) The ErbB family consists of four receptors which bind a suite of ligands with varying specificity. Ligand binding promotes homo- and hetero-dimer formation, autophosphorylation, and downstream signaling involving both cytoplasmic kinases and transcriptional changes. (B) Multiple protective mechanisms are triggered by ErbB activation, including ERK MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling. These cascades restrict apoptosis, promote proliferation and migration, maintain barrier integrity, and contribute to immune system regulation. Metalloproteinase-dependent ErbB ligand cleavage and release can be triggered by extracellular signals such as probiotic/commensal bacteria (Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG shown as example). However, inflammatory cytokines can inhibit expression of multiple ErbB ligands, potentially limiting responses in the absence of exogenous ligand.