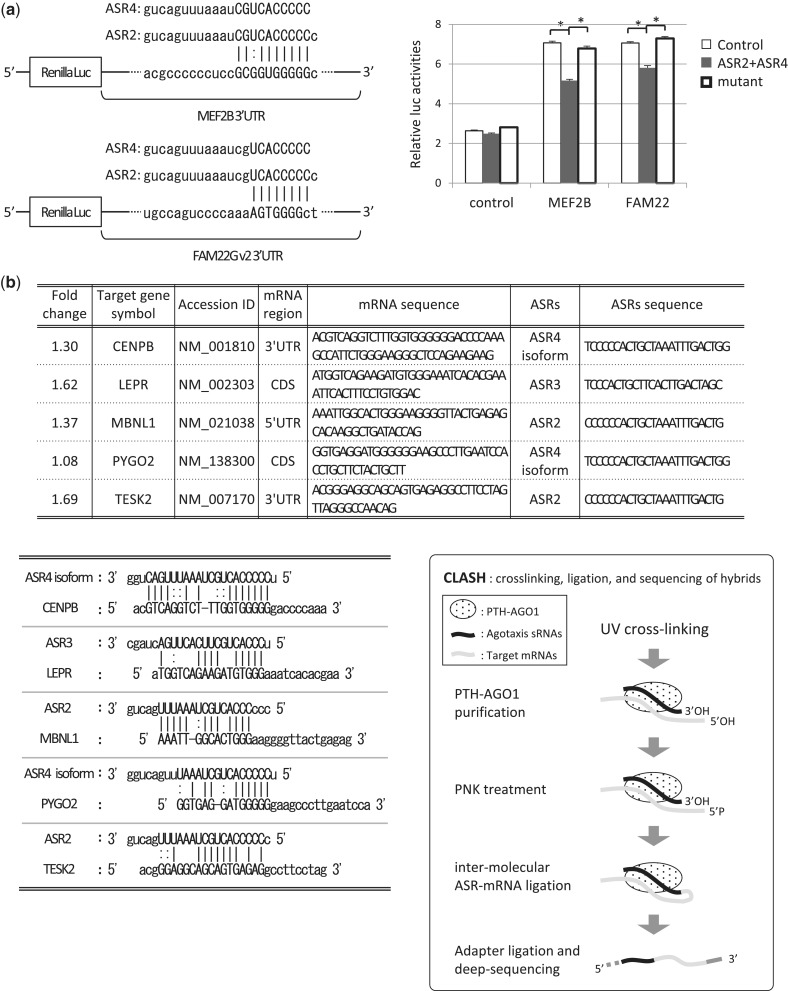
Figure 5.
ASRs can bind and silence targets. (a) MEF2B and FAM 22 were regulated by ASR2 and ASR4 though their 3′ UTR. The putative target sequence of ASR2 and 4 in MEF2B and FAM22-3′ UTRs (left). Reporter vectors were constructed by inserting MEF2B and FAM22-3′ UTRs into Renilla luciferase in a psiCHECK2 vector. Renilla to firefly luciferase ratios are shown (right). All binding sites caused ASR2- and 4-dependent downregulation but not control or mutant (agggggacuaaauuugacgg) (*P < 0.05). (b) The sequence-specific binding of ASRs at the CDS, 3′ UTR and 5′ UTR of the target mRNAs in 293T cells, which were revealed by CLASH and downregulated in Ago1 knockdown L591 cells. The five genes, which have putative target sequences of ASRs in the mRNAs, were bound by ASRs in 293T cells, and upregulated by Ago1 knockdown in L591 cells are listed (upper). The putative target sequences of ASRs in the target mRNAs are shown (lower left). Overview diagrams of ASRs-mRNA chimera preparation (lower right). AGO1-associated sRNAs including ASRs and target mRNAs were cross-linked to PTH-AGO1 by UV exposure. The protein–RNA complexes were purified. mRNA 5′ ends were phosphorylated with PNK treatment and ligated to associated ASRs. Finally, 5′ and 3′ adapters were ligated to the chimeric RNAs for next-generation sequencing.