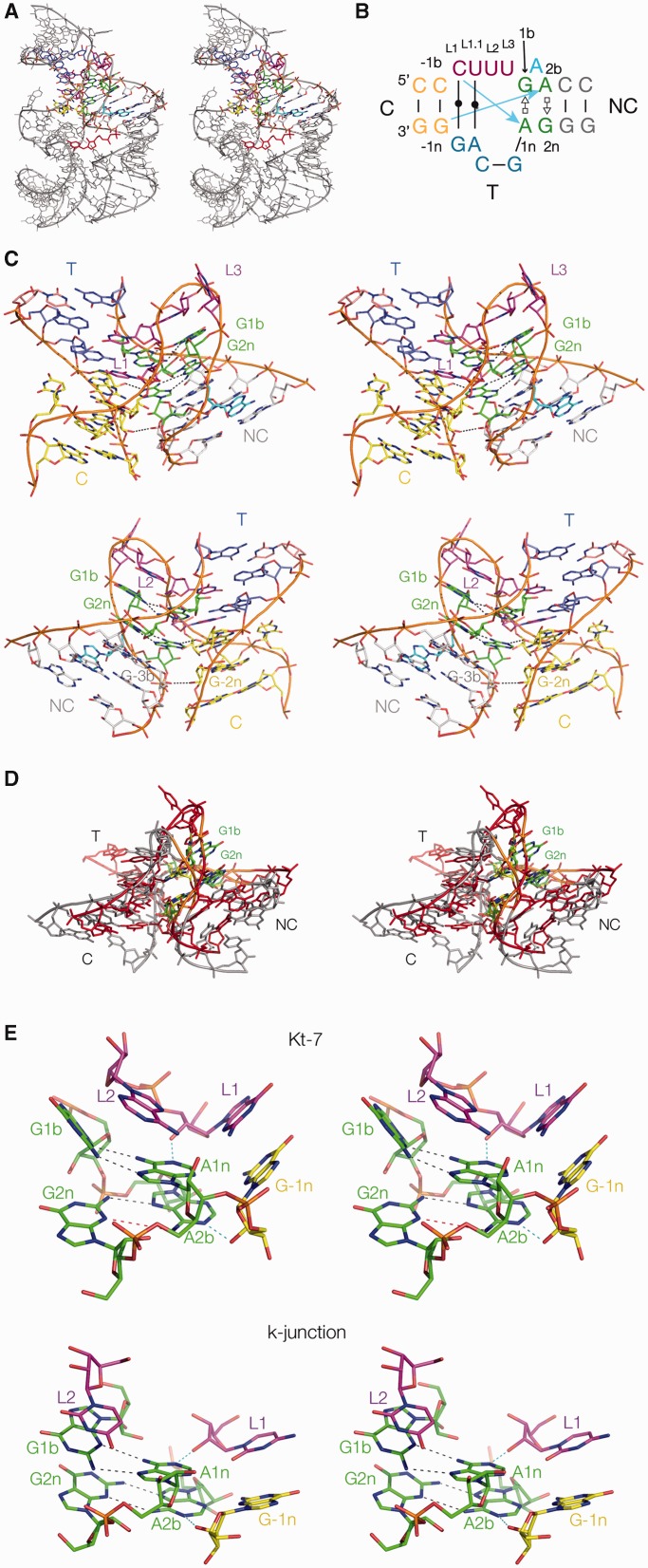
Figure 2.
The A.thaliana TPP riboswitch and the k-junction. (A) The whole riboswitch, with the k-junction highlighted in colour. The structure was determined by Ban and coworkers (20,21), and all molecular graphics images generated from PDB file 3D2G, shown as parallel-eye stereo pairs. The TPP ligand is highlighted in red. (B) The sequence and secondary structure of the k-junction. Nucleotides are coloured in the same manner as in the molecular graphics images, and the blue arrows indicate the standard cross-strand hydrogen bonds found in most k-turns. The nucleotides are labelled to follow our standard nomenclature for a simple k-turn (13). (C) The TPP riboswitch k-junction. Two views are shown, from the side of the bulged strand (upper) and that of the T helix (lower). The ribbon shows the path of the three strands forming the junction. The T and C helices are coaxial, with continuous base stacking through the point of strand exchange with the NC helix. Note the interaction of the adenine that is interposed between G1b and A2b (coloured cyan) in the major groove of the NC helix, hydrogen bonding with the Hoogsteen edge of A5n, forming a triple-base interaction with the 5b•5n pair. (D) Superposition of the k-junction with a standard N1-class k-turn. The k-junction is coloured red with 1b•1n and 2b•2n pairs green, while H. marismortui Kt-7 as found in the ribosome is coloured grey with 1b•1n and 2b•2n pairs yellow. (E) A comparison of the key interactions at the core of a standard N1-class k-turn (H. marismortui Kt-7 in the ribosome, upper) with those found in the k-junction (lower). The two key cross-strand hydrogen bonds are highlighted in cyan. In Kt-7 the A2bN6-G2nN3 distance is 4.7 Å (coloured red), i.e. too long to be hydrogen bonded.