Figure 3.
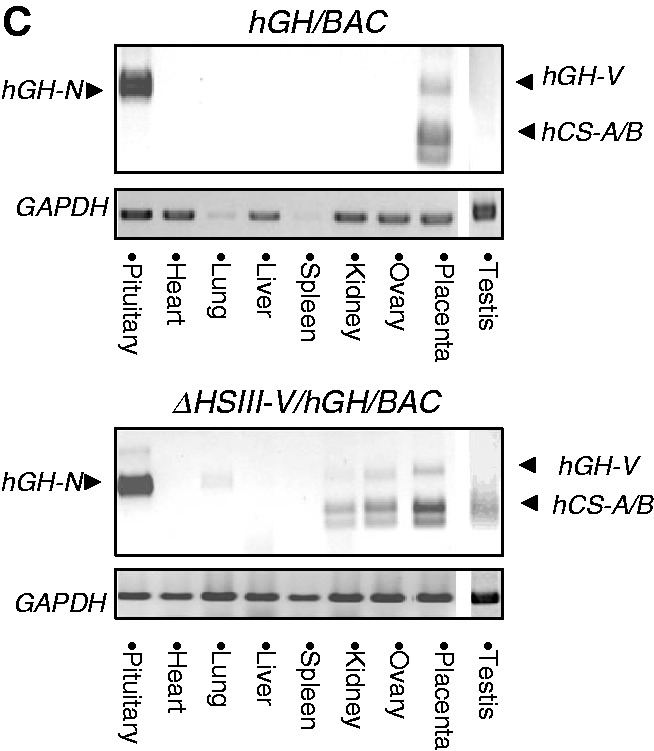
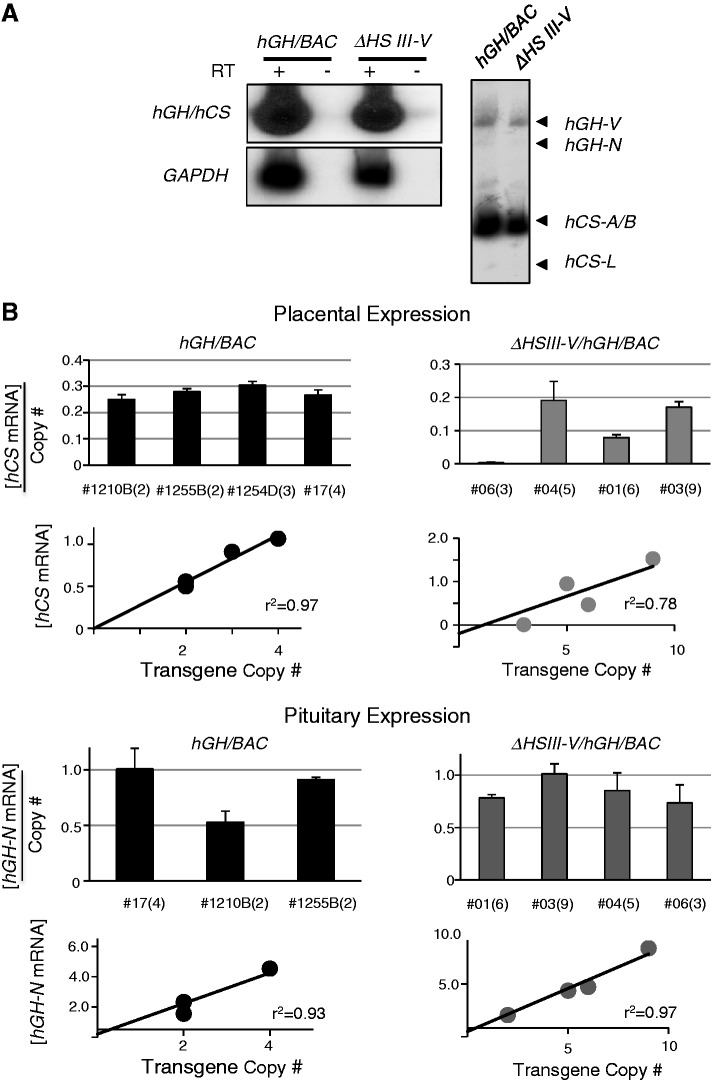
The HSIII-V region played an essential role in protecting the hGH transgene locus from site-of-integration effects in the placenta. (A) hCS mRNAs were robustly expressed from the ΔHSIII-V/hGH/BAC transgene. RT/PCR (left) and coRT/PCR-TaqI (right) analyses confirmed robust and appropriately selective expression of the hCS genes in the transgenic mouse placenta (analyses as in Figure 2B and 2C). (B) Deletion of the HSIII–V region rendered transgenic expression sensitive to site-of-integration effects in the placenta but not in the pituitary. (Top) Placental studies. Expression of hCS mRNAs in the placenta of four structurally-intact hGH/BAC lines and in four ΔHSIII-V/hGH/BAC lines was determined by RT/Q-PCR. The values were each normalized to the corresponding levels of GAPDH mRNA and then normalized to transgene copy-number (shown as mean + SD, n = 3). The copy number for each line is shown in parentheses next to the respective line designations. Regression analyses of the two sets of data, shown below the corresponding histograms, evaluated the correlation between total hCS mRNA expression (mean, n = 3) and copy number. The comparison of the linear regression r2-value for the hGH/BAC and the ΔHSIII-V/hGH/BAC lines (0.97; P-value 0.02 and 0.78; P-value 0.11) revealed a significant loss of copy-number dependence of transgene expression subsequent to deletion of the HSIII-V region. (Bottom) Pituitary studies. RT/Q-PCR analysis of pituitary hGH-N mRNA was normalized to GAPDH mRNA and transgene copy number (as in placental samples, above). The histogram represents the average of expression from triplicate assays of the indicated lines (+SD). The regression analyses of the data are shown below the histograms with high r2-values for both the intact hGH/BAC and ΔHSIII-V/hGH/BAC transgenic lines. (C) Deletion of the HSIII–V region triggered ectopic expression of hCSs. Tissue surveys from an intact hGH/BAC line (#1255B) and a ΔHSIII-V/hGH/BAC line (#01) are shown. RNAs were subjected to the coRT/PCR-TaqI analysis. These studies revealed widespread ectopic expression of hCS mRNAs from ΔHSIII-V/hGH/BAC transgene. In contrast, hGH-N mRNA expression remained tightly restricted to the pituitary in both lines.