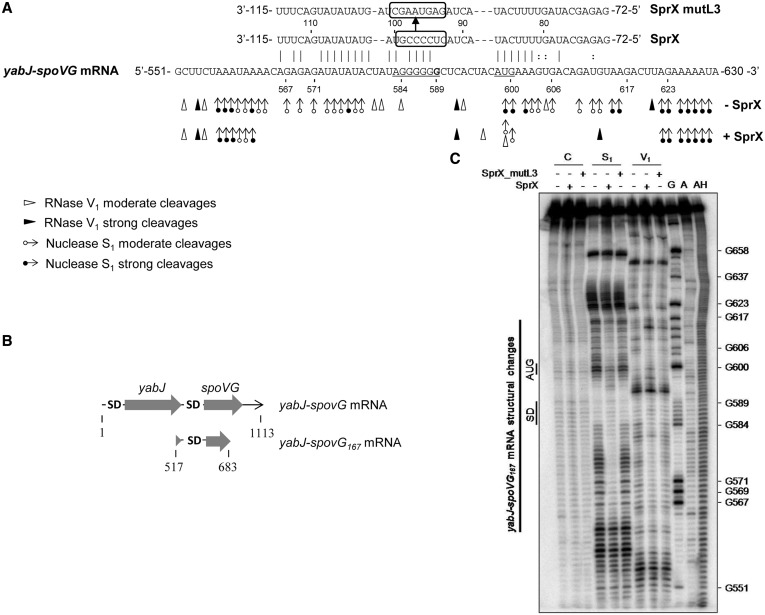
Figure 3.
SprX interacts directly with the yabJ-spoVG mRNA by base-pairing at the spoVG RBS. (A) SprX base pairings with the yabJ-spoVG mRNA. Binding of SprX encompasses the spoVG translational initiation site within the yabJ-spoVG mRNA. The SD sequence (5′-AGGGGG-3′) and initiation codon are underlined. The cleavage site of yabJ-spoVG mRNA corresponding to G at position 589 (9) is indicated in bold. We outline the mutated nucleotides in SprX_mutL3 for 5′-GAGUAAGC-3′. Probing data in the absence (−SprX) and in the presence of SprX (+SprX) are indicated. Enzymatic cleavages are as follows: moderate (white circle with rightward arrow) and strong (black circle with rightward arrow) S1 Nuclease cleavages; moderate (white right-pointing pointer) and strong (black right-pointing pointer) RNase V1 cleavages. (B) Schematic representation of yabJ-spoVG167 mRNA. The two ORFs and the two SD sequences are indicated. (C) Structural probing of the yabJ-spoVG167 mRNA in the presence and absence of SprX. Enzymatic hydrolysis (RNases S1 and V1) of 5′-end-labeled yabJ-spoVG167 mRNA free (−) or with an excess of either SprX or SprX_mutL3. Lanes are as follows: C, control; S1, nuclease S1; V1, RNase V1; G, RNase T2; A, RNase U2; and AH, alkaline ladder. The bar denotes the localization of the main reactivity changes that are induced by complex formation with SprX but not with SprX_mutL3.