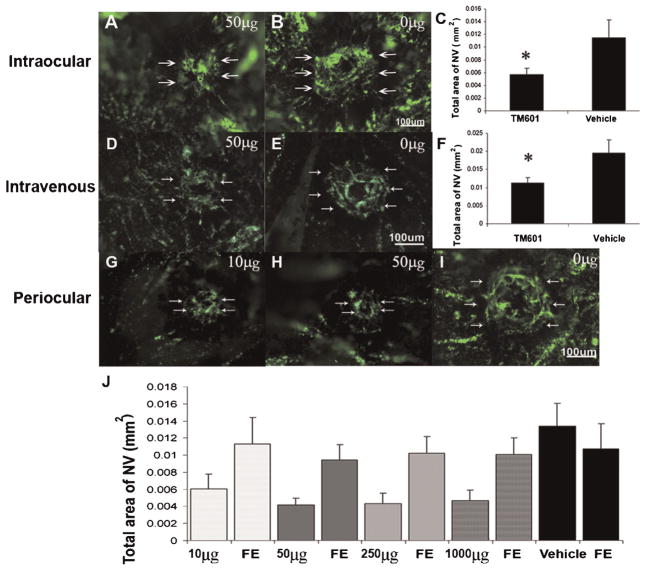
Fig. 1.
TM601 given by intraocular, intravenous, or periocular injections suppresses choroidal neovascularization (NV). Mice had laser photocoagulation-induced rupture of Bruch’s membrane and then received an intraocular injection of 1 μl of vehicle or vehicle containing 50 μg of TM601. After 14 days, mice were perfused with fluorescein-labeled dextran and the area of choroidal NV at Bruch’s membrane rupture sites was visualized by fluorescence microscopy of choroidal flat mounts and measured by image analysis. Other groups of mice had rupture of Bruch’s membrane followed by tail vein injections of vehicle or 20 mg/kg of TM601 three times a week. The area of choroidal NV appeared smaller in eyes injected with TM601 (A) compared to those injected with vehicle (B). Statistical comparison using a mixed-effects model showed that the mean (±SEM) area of choroidal NV at Bruch’s membrane rupture sites determined by image analysis with the investigator masked with respect to treatment group was less in eyes injected with TM601 compared to those injected with vehicle (C, P = 0.013). The area of choroidal NV was also significantly reduced in mice that received intravenous injections of TM601 compared to mice that received intravenous injections of vehicle (D–F, P = 0.024). Several different doses of TM601 were given by daily periocular injection. Representative images from eyes injected with 10 μg (G) or 50 μg (H) of TM601 show smaller areas of choroidal NV than a representative image from vehicle-injected eyes (I). Compared to eyes treated with vehicle, the mean (±SEM) area of choroidal NV at Bruch’s membrane rupture sites was significantly less in eyes treated with daily periocular injections of each of the doses of TM601 (J, P = 0.008, 0.001, 0.001, and 0.002 for 10, 50, 250, and 1,000 μg, respectively). Eyes treated with 50 μg (P = 0.007), 250 μg (P = 0.03), or 1,000 μg (P < 0.001) ofTM601 had significantly smaller areas of choroidal NV than their corresponding untreated fellow eyes (FE). There was no significant difference in area of choroidal NV in eyes treated with 10 μg ofTM601 compared to corresponding fellow eyes (P = 0.147).