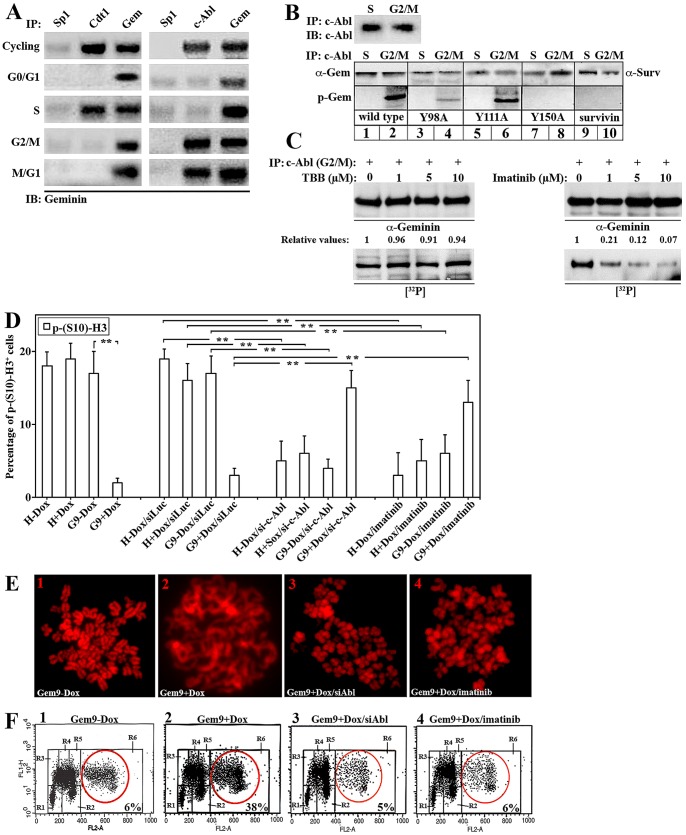
Figure 1. c-Abl binding and phosphorylation of geminin Y150 in G2/M/early G1 cells promotes overexpressed geminin oncogenicity in HME cells.
(A) Immunoprecipitation of cycling, G0/G1, S, G2/M or M/G1 HME cells with anti-Cdt1, -c-Abl, -Sp1 (negative control) and -geminin antibodies. (B) c-Abl immunoprecipitated from S or G2/M HME cells (upper panels) was used to in vitro phosphorylate GST-WT-, -Y98A-, -Y111A-, -Y150A-geminin or GST-survivin (negative control, lower panels). (C) c-Abl immunoprecipitated from G2/M was used to in vitro phosphorylate GST-WT-geminin in the presence of the increasing concentrations of CKII inhibitor, TBB (left panels) or c-Abl inhibitor, imatinib (right panels). (D) The percentage of p-(S10)-H3+-cells in HME, uninduced or induced Gem9 following transfection of si-control or si-c-Abl (for 72 hr) or treatment with vehicle or 5 µM of imatinib (during the last 24 h). Data are represented as mean ± SD of triplicates done three separate times, where * = p≤0.05 and ** = p≤0.001. (E) Metaphase spread analysis of chromosome condensation in uninduced or induced Gem9 cells before or after transfection of sic-Abl or treatment with 5 µM of imatinib. (F) FACS analysis of uninduced or induced Gem9 cells transfection of sic-Abl or treatment with 5 µM of imatinib. Aneuploid cells are shown in the red circles and their percentage is in insets. R1 = G0/G1, R3/R4/R5 = early/mid/late S, R2 = G2/M and R6 = >4N cells. Experiments were done three separate times in triplicates.