Figure 2. ino80is required for viability during metamorphosis.
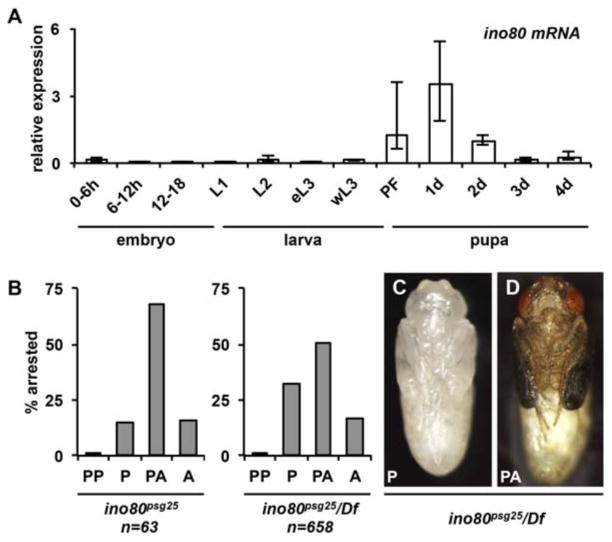
(A) qPCR analysis of ino80 mRNA expression throughout development. The highest expression levels are observed at the onset of metamorphosis, from puparium formation to 2 days after puparium formation (APF). Animals staged from egg lay for embryonic (0-6, 6-12 and 12-18 hours after egg lay (AEL)) and larval stages (L1: 30-42 AEL, L2: 54-66 AEL, eL3: 76-88 AEL). wL3 identified by robust expression of Sgs3-GFP. Stages during metamorphosis were synchronized at puparium formation (PF) and collected in 24-hour intervals. y-axis plots relative expression compared to 2 days APF; x-axis denotes the developmental stage analyzed. Three independently-isolated whole animal samples were run for each time point and target genes were normalized to rp49. (B) Lethal phase analysis of homozygous and hemizygous ino80psg25 mutant animals. Most homozygous and hemizygous ino80psg25 mutant animals die after head eversion, as either pupae or pharate adults. A smaller fraction eclose as adults. (C-D) Hemizygous ino80psg25 mutant animals that arrest as pupae (C) or pharate adults (D) have normal morphology, with head eversion and extension of wings and legs. Animals were dissected out of their pupal cases and imaged at their respective terminal stages. PF=puparium formation, PP=prepupa, P=pupa, PA=pharate adult, A=eclosed adult.
