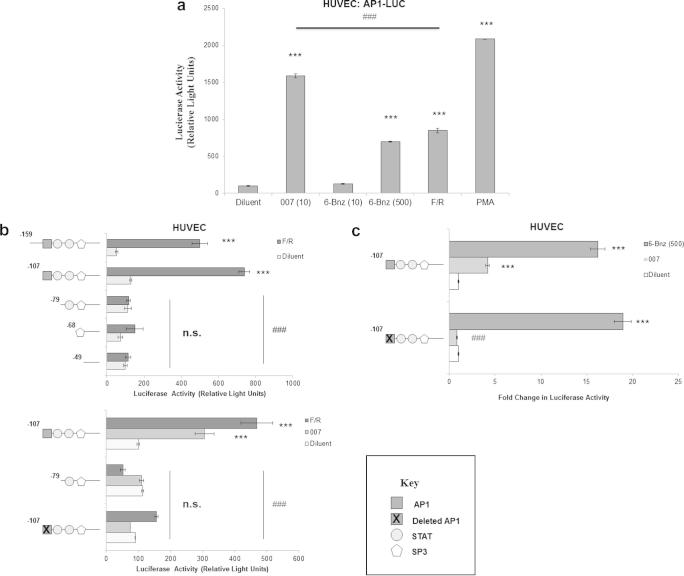
Fig. 1.
EPAC1 activation promotes AP1-dependent transcription of the SOCS3 gene in HUVECs. (a) HUVECs were transfected with an AP1 luciferase reporter construct and then stimulated with the EPAC-specific agonist 007 (10 μM), the PKA-specific agonist 6-Bnz (at either 10 μM or 500 μM, as indicated), a combination of the adenylate cyclase activator forskolin (10 μM) and the cyclic AMP-specific phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram (10 μM), or the protein kinase C activator, PMA (100 nM). Cell extracts were then prepared and luciferase activities measured as described in Section 2. Significant differences relative to diluent-treated cells are indicated, ∗∗∗P < 0.001 (n = 3), as are significant increases in 007-treated cells compared to those treatment with 6-Bnz or F/R, ###P < 0.001. (b) HUVECs were transfected with luciferase constructs containing deletions and truncations of the murine SOCS3 promoter. Cells were then stimulated for 16 h with either F/R or 007 (lower panel). Cells extracts were then assayed for luciferase activity. Significant differences relative to diluent-treated cells are indicated, ∗∗∗P < 0.001, as are significant decreases in luciferase activity relative to F/R-treated cells, ###P < 0.001 (n = 3). (c) HUVECs were transfected with the minimal murine SOCS3 promoter or the minimal promoter with disruptive deletions in the putative AP1 site. Cells were then stimulated with either 6-Bnz (500 μM) or 007 (10 μM). Cell extracts were then assayed for luciferase activity and significant differences relative to diluent-treated cells are indicated ∗∗∗P < 0.001; as are significant differences relative to 007-treated cells transfected with minimal promoter vs. with AP1-mutated constructs, ###P < 0.001 (n = 3).