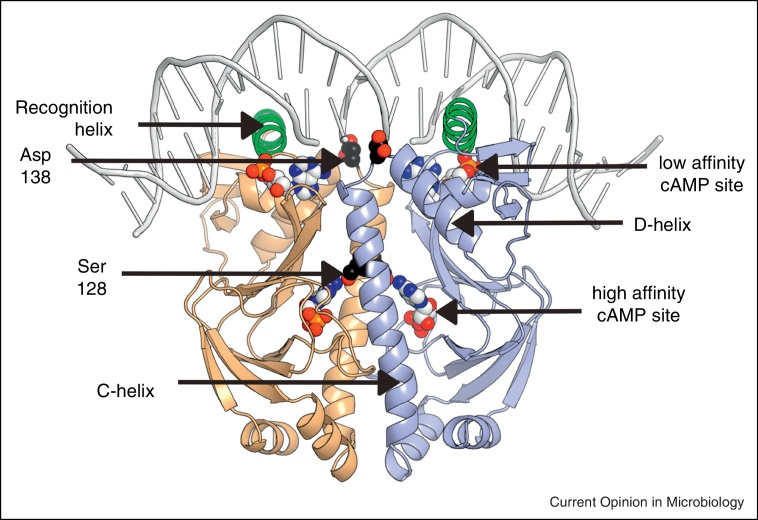
Figure 1.
Relevant structural features of the E. coli CRP–cAMP–DNA complex. The CRP dimer (one protomer in brown, the second in blue) is shown in cartoon representation with the DNA-recognition helices highlighted in green. The locations of the C-helices at the dimer interface, the D-helices of the DNA-binding domain and the key residues Ser-128 and Asp-138 are indicated. Cyclic-AMP molecules bound in the anti-conformation at the higher affinity sites in the sensory domain and in the syn-conformation at the low affinity sites close to the DNA are shown in a ‘space-fill’ representation. DNA is shown as a pale gray ribbon. The diagram was constructed using Pymol [34].