Figure 5. Targeting apoptosis via the BCL-2 family in biology and disease.
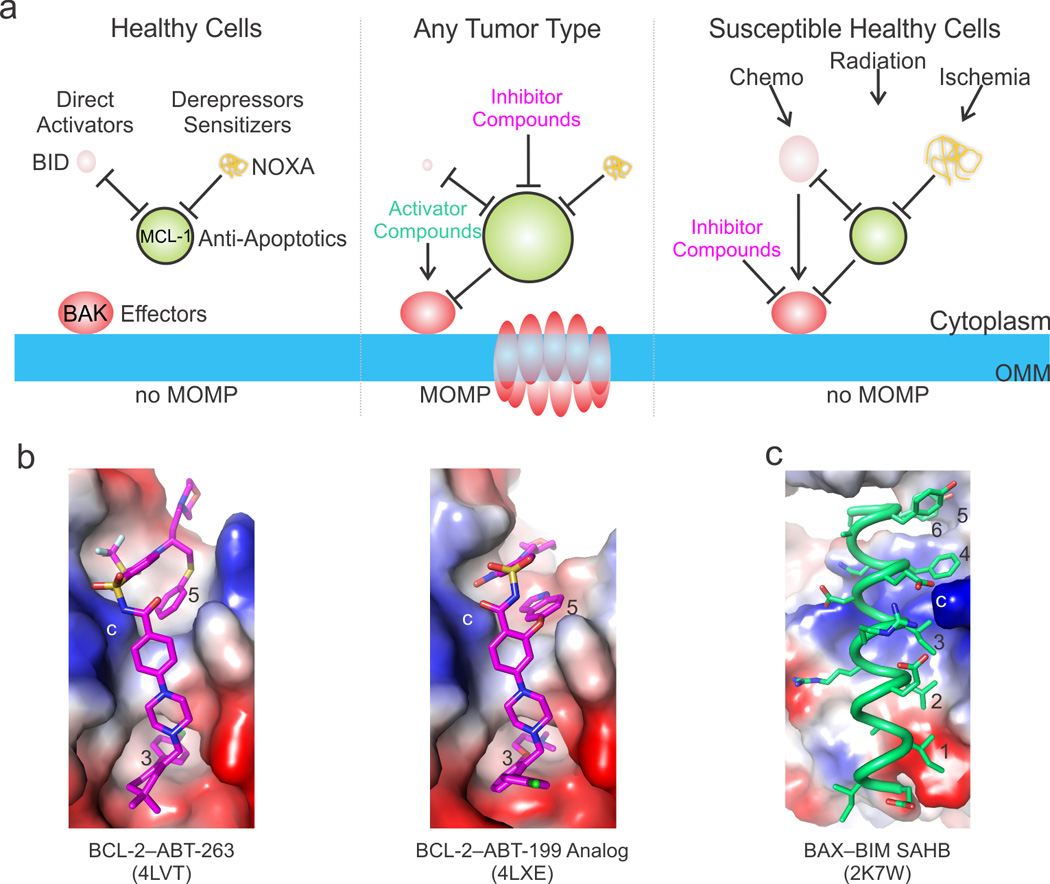
a) Targeted apoptotic therapy addresses the upregulation of anti-apoptotic and the downregulation of activator BCL-2 family proteins in cancer and the aberrant overactivation of the pathways during pathological insults and toxicity related stress. We illustrate this be varying the size of the BCL-2 family protein cartoons to reflect the fluctuations in intracellular levels. For example, in healthy cells the BH3-only protein levels are low and their pro-apoptotic activities are kept in check by anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins, overall preventing the direct activator–effector axes from being engaged (left panel). In tumors, the BH3-only proteins are down-regulated and the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins are upregulated, together preventing MOMP. Compounds that mimic the activities of BH3-only proteins can be used to activate the effectors and inhibit the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 proteins (middle panel). On the other hand, compounds that inhibit the effectors may be used to block excessive cell death in healthy tissues susceptible to chemotherapy and radiation therapy or in healthy or diseased tissues prone to ischemic cell death. b) The most promising therapeutics have been designed at Abbvie for the anti-apoptotic BCL-2 family proteins, including ABT-263, which targets both BCL-2 and BCL-xL, and the BCL-2-specific compound ABT-199. Both compounds take advantage of scaffolds that engage the BC groove from the third hydrophobic contact (occupied by a conserved Leu in BH3 ligands) to beyond the fifth. These compounds have also been engineered to explore the electrostatic landscape of the BC groove, including a similar charge interaction to the conserved Arg–Asp (labeled *). c) BH3 mimetics for the non-canonical interaction described for the stabilized alpha helix of BCL-2 protein BIM (SAHB) at a groove on BAX distantly resembling the BC groove have also been described, and either SAHBs or their small molecule mimetics may trigger BAX. Importantly, both BAK- and BAX-mediated MOMP require activation by engagement of their BC grooves, which provides additional opportunities for modulating the mitochondrial pathway with activators or inhibitors. Positive, negative, and neutral (hydrophobic) patches are blue, red, and white, respectively.
