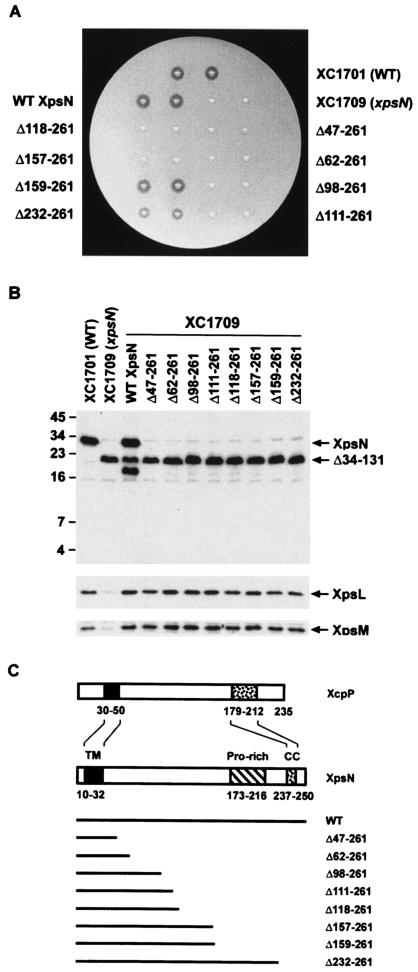
FIG. 1.
(A) Starch plate assay of XpsN C-terminal deletion mutants. The xpsN mutant strain XC1709 containing plasmids, each encoding a C-terminally truncated XpsN protein, was assayed for extracellular α-amylase secretion on a starch plate. After overnight incubation at 28°C, the clear zone surrounding the colony was scored as positive secretion. Wild-type (WT) XC1701 and the xpsN mutant XC1709 (xpsN) were included as positive and negative controls, respectively. WT XpsN, XC1709 complemented with the wild-type XpsN. (B) Immunoblot analysis of total lysates for abundances of XpsL, XpsM, and XpsN. XC1709 containing plasmids, each encoding a C-terminally truncated XpsN protein, was analyzed by Western blotting with anti-XpsN antibody (top), anti-XpsL antibody (middle), or anti-XpsM antibody (bottom). The molecular mass standards (in kilodaltons) are shown on the left. (C) Schematic diagram of deletion mutants, aligned with the full-length XpsN and the XcpP protein of E. chrysanthemi. The positions of the TM region, the proline-rich region (Pro-rich), and the predicted coiled-coil (CC) are marked with residue numbers indicating positions in the respective protein.