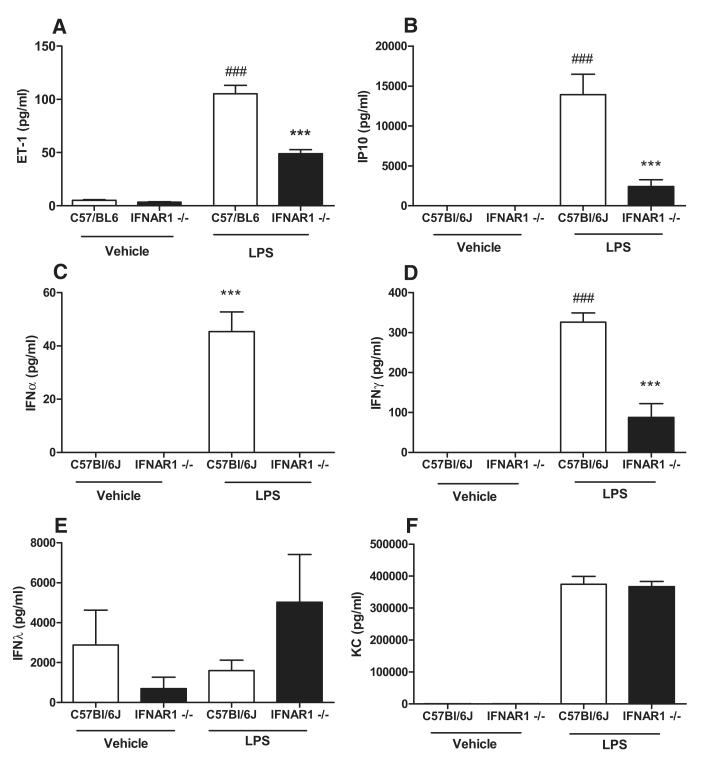
Figure 8.
Influence of type I interferon (IFN) signaling on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced endothelin 1 (ET-1) generation explored using mice lacking a functional type I IFN receptor. Mice lacking a functional type I IFN receptor (IFNAR1−/−) injected with either LPS or vehicle control for 4 hours and compared with wild-type (C57Bl/6J) mice. Data presented as mean±SEM from n=6 mice. Serum levels of ET-1 (A), interferon γ inducible protein 10 (IP10) (B), IFNα (C), IFNγ (D), IFNλ (E), and keratinocyte-derived chemokine (KC) (F) were measured. Statistical significance determined by 1-way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni multiple comparison post-test (###P<0.0001 for LPS vs Vehicle) and (***P<0.0001 for IFNAR1−/− vs C57Bl/6J mice).