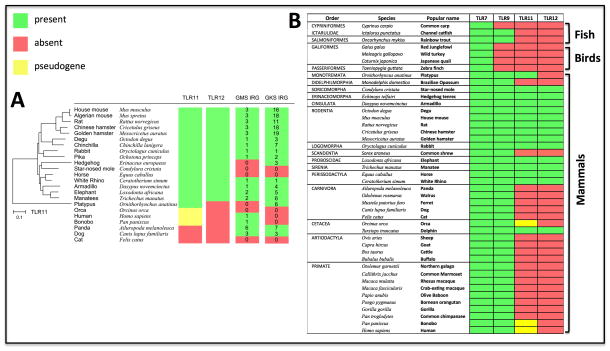
Figure 3. Distribution of TLR11, TLR12 and IRG protein genes in mammalian species.
(A) Phylogenetic tree of TLR11 and overlapping expression of TLR12 as well as IRG GMS and IRG GKS gene families. (B) Ubiquitous versus confined distribution of TLR7/TLR9 and TLR11/TLR12 genes in vertebrate genomes, respectively. TLRs 7, 9, 11 and 12 coding sequences were downloaded from Genbank from species that have complete genome sequences. Retrieved sequences from mammals, fishes and birds were analyzed by ORFfinder (http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gorf/gorf.html) to identify pseudogenes by looking for frameshifts or premature stop codons. Multiple and global sequence alignments for each TLR were performed by Muscle. Neighbor-joining trees were designed by MEGA 5.2.2 from Muscle alignments.