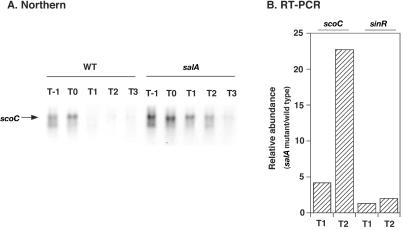
FIG. 5.
Abundance of scoC transcripts in a salA-deficient mutant compared with that in the wild-type strain. Strains used were CU741 and OM210 for the wild-type (WT) and salA strains, respectively. The procedures for RNA isolation and Northern and RT-PCR analyses are described in Materials and Methods. The RNA samples for the Northern and RT-PCR analyses were prepared separately. (A) Northern analysis. Cells were grown in Schaeffer's sporulation medium, and samples (20 ml) were withdrawn from T−1 to T4. Twenty micrograms of the isolated RNAs was applied to each lane, and scoC transcripts were detected with a digoxigenin-labeled PCR probe. In a separate experiment we have confirmed that there was no detectable band corresponding to the scoC transcript in the RNA samples obtained from strain OM213 (scoC). (B) RT-PCR analysis. Levels of mRNAs for scoC and sinR were quantified at T1 and T2 by using 1 μg each of the RNA samples. The oligonucleotide pairs ScoC-1 and ScoC-2 and SinR-F and SinR-R2 were used to detect sinR and scoC mRNAs, respectively. Relative abundance of mRNA at each stage was determined by dividing the mRNA levels in the mutant cells by those estimated in the wild-type cells.