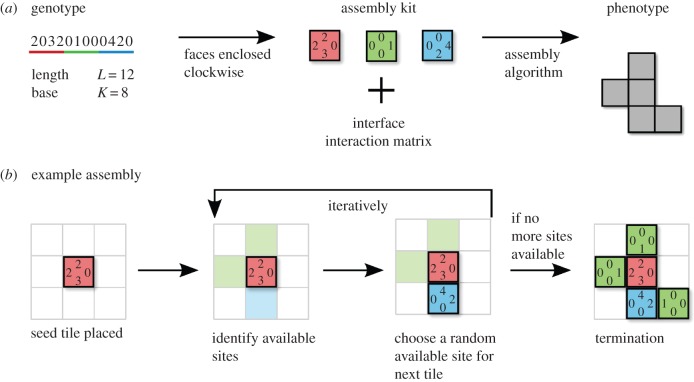
Figure 3.
The Polyomino GP map. (a) The translation from an example genotype to phenotype is depicted, with the intermediate conversion into an assembly kit shown. In the genotype, the characters are underlined with the colour of the block they are assigned to. The interface interaction matrix is not shown explicitly, but throughout our work we assume the convention of interface types interacting in pairs (1 ↔ 2, 3 ↔ 4 … ), with 0 and c − 1 being neutral. The interaction matrix together with the assembly kit are passed to the assembly algorithm, which is used to produce the phenotype. (b) An example of the assembly process is shown, which proceeds in discrete time steps. The first tile in the assembly kit is used to seed the assembly. Further time steps follow, with the identification of available sites (depicted in light green and blue in the second picture from left), followed by the random choice of an available site and placement of the corresponding tile (a blue tile is placed on the blue available site in this example). Assembly is terminated when there are either no more available sites (as above), or if the structure is larger than Dmax (number of blocks) in width or height after which we assume the structure will no longer terminate but grow indefinitely.