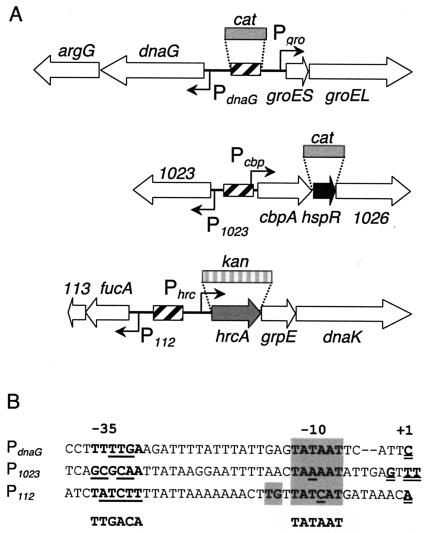
FIG. 1.
(A) Structural organization of H. pylori chaperone genes and divergent genes and operons. Hatched boxes represent positions of HspR-binding sites. Open arrows indicate genes; solid and gray arrows indicate regulatory genes. All genes are marked according to their name or by the numbers of the genome sequence published by Tomb et al. (38); groES and groEL form a transcriptional unit (16) and code for the HspA (Hsp10) and HspB (Hsp60) proteins. hrcA, grpE, and dnaK are transcribed as part of a tricistronic transcript (16) and code for a homologue of the HrcA repressor of B. subtilis and the GrpE and DnaK (Hsp70) chaperones, respectively. cbpA codes for a homologue of cochaperone curved DNA-binding protein CbpA of E. coli (39), hspR codes for the negative regulator of the Pgro, Pcbp, and Phrc promoters (35), and hp1026 codes for a protein with homology to a putative helicase-like protein from H. influenzae. dnaG encodes DNA primase, argG encodes argininosuccinate synthase, hp1023 encodes a putative outer membrane protein, hp112 encodes a protein with 30% (50 of 164) amino acid identity to a putative fuculose-1-phosphate aldolase of Aquifex aeolicus, and hp113 encodes a protein of unknown function. (B) Nucleotide sequences and transcription start sites of divergent promoters. Alignment of the promoter sequences with respect to their transcriptional start site (+1) is shown. Putative −10 hexamers are boxed. The Eσ70-recognized sequence is indicated (3); mismatches with respect to this sequence are underlined. The P112 promoter contains a TG motif at positions −14 and −15 typical of so-called extended −10 promoters (20). The P112 start site of transcription is located in the putative coding region of hp112 as annotated by Tomb et al. (38). Possible alternative ATG or GTG start codons can be found at nucleotide positions +3, +69, and +138 with respect to the P112 start site of transcription; no obvious corresponding ribosome-binding sites can, however, be detected.