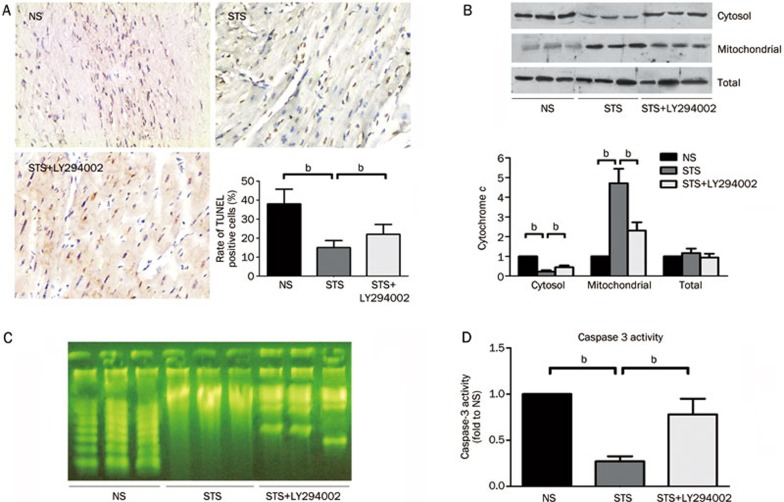
Figure 2.
The effect of STS on myocardial apoptosis after ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury. (A) Representative photomicrographs demonstrating TUNEL staining for apoptotic cells in the rat heart at 2 h after reperfusion in the NS, STS, and STS+LY294002 groups. The effects on the severity of cardiac apoptosis are shown in an average quantitative analysis of the rate of TUNEL-positive cells. The data are represented as the mean±SEM. n=8 for each group. bP<0.05 was considered statistically significant among each group. (B) Cytochrome c levels in the cytosol, mitochondrial and total fraction were analyzed by WB and semi-quantitatively estimated as the fold-change relative to the NS group. (C) The detection of internucleosomal DNA fragmentation using gel electrophoresis and Biotekepeter Ultra power staining in the NS, STS, and STS+LY294002 groups. (D) The effects of STS with or without LY294002 treatment on caspase 3 activity in area at risk zone of the cardiac tissues at 2 h after reperfusion, quantitatively estimated as the fold-change relative to the NS group. bP<0.05 is considered significant difference among each groups.