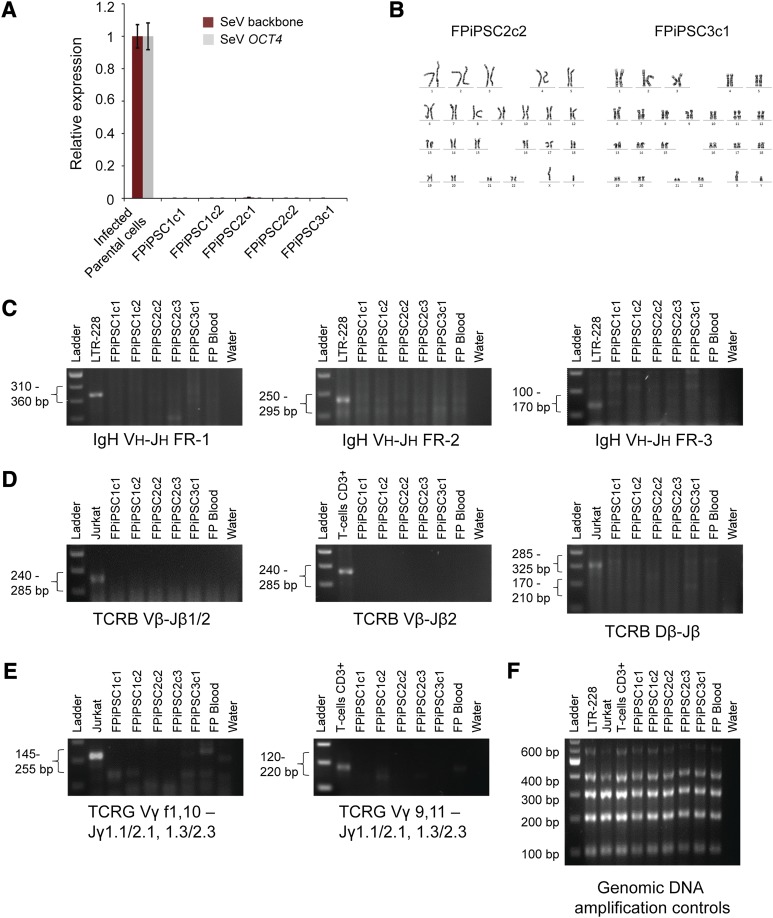
Figure 3.
Characterizations of the FPiPSCs. (A): Transgene expression analysis of the FPiPSC lines derived. The SeV backbone and SeV OCT4 expression values were measured by quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction and normalized to SeV-infected parental cell with β-ACTIN as internal control. No SeV transgene was detected in the total RNA harvested from these human induced pluripotent stem cell lines. (B): Cytogenetic analysis on FPiPSCs. The FPiPSCs showed normal human karyotype with 46 chromosomes. (C): IgH rearrangement analysis on the FPiPSC clones. LTR-228 (B-cell line) was used as a positive control. No IgH recombination was observed in our FPiPSCs. (D): TCRB rearrangement analysis on the FPiPSC clones. Jurkat (T-cell line) or CD3+ T cells were used as positive controls for this analysis. (E): TCRG rearrangement analysis on the FPiPSC clones. Jurkat cells (T-cell line) or CD3+ T cells were used as positive controls for this analysis. Negative results from all the V(D)J rearrangement polymerase chain reaction (PCR) imply that the FPiPSCs derived did not originate from B or T lymphocytes. In (C), (D), and (E), the expected PCR product range was stated on the left and the target regions were indicated below the gel images. The finger-prick blood used in this assay had been cultured in cell expansion medium for at least 15 days before being harvested. A water sample was always included in the PCR analysis as a negative control. (F): The genomic DNA amplification control experiment was performed on all the samples used in these V(D)J rearrangement analyses. Abbreviations: FPiPSC, finger-prick-derived induced pluripotent stem cell; SeV, Sendai virus; TCR, T-cell receptor.