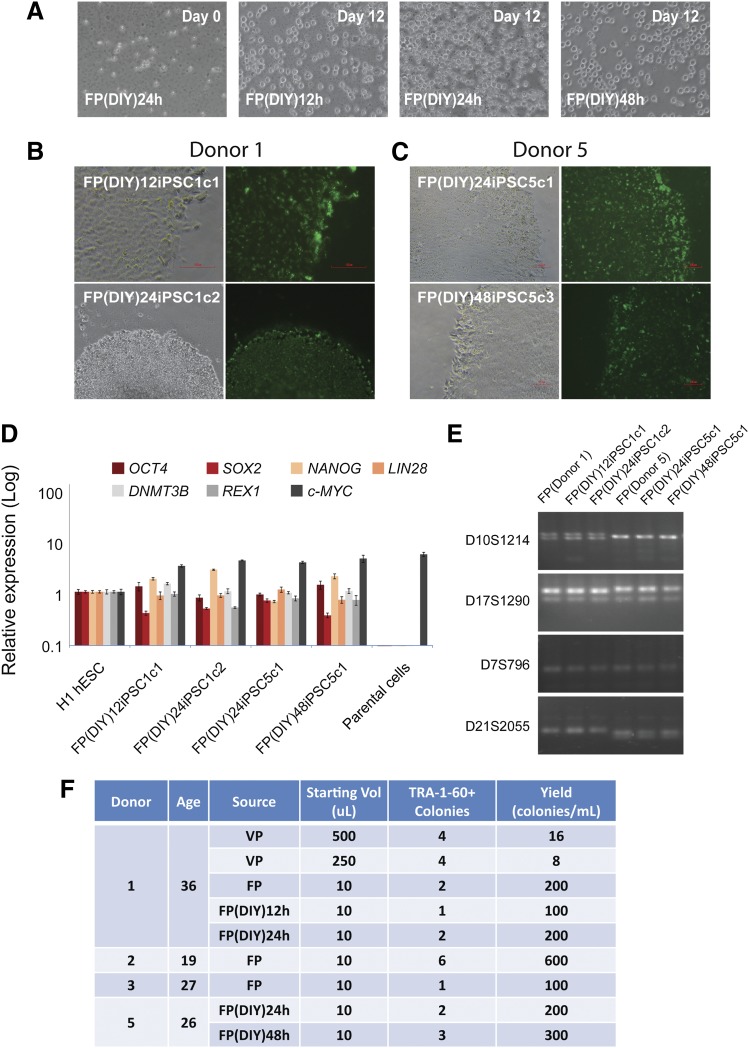
Figure 4.
DIY concept for finger-prick-derived induced pluripotent stem cell (FPiPSC) generation. (A): FP blood samples collected 12 hours, 24 hours, and 48 hours before cell culture. The cells were red blood cell-lysed at day 0 (left) and expanded for 12 days in medium. All images were acquired with original magnification ×20 objectives. (B): Human induced pluripotent stem cell (hiPSC) colonies derived from donor 1 DIY FP blood (12 hours and 24 hours) stained positive for a pluripotency marker, TRA-1-60. The upper image was acquired with original magnification ×20 objectives, whereas the lower image was acquired with original magnification ×4 objectives. (C): hiPSC colonies derived from donor 5 DIY FP blood (24 hours and 48 hours) stained positive for a pluripotency marker, TRA-1-60. All images were acquired with original magnification ×10 objectives. (D): Quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analyses for the expression of embryonic stem cell (ESC) marker genes OCT4, SOX2, NANOG, LIN28, DNMT3B, REX1, and c-MYC in FP(DIY)iPSCs, H1 ESCs, and parental cells. Individual polymerase chain reactions (PCRs) were normalized to H1 ESC and β-ACTIN as internal control. All the FP(DIY)iPSC lines examined showed similar expression of ESC marker genes to that of H1 ESCs. (E): DNA fingerprinting analysis confirms that FPiPSC lines are derived from their parental lines. PCR primer sets D10S1214, D17S1290, D7S796, and D21S2055 were used to detect for variable tandem repeats. (F): Summary of hiPSCs derived from donors. The VP and FP indicated were the venipuncture blood and finger-pricked blood, respectively. The reprogramming yield was calculated based on the TRA-1-60 colonies observed and normalized to 1 ml of blood. Abbreviations: DIY, do-it-yourself; FP, finger prick; hESC, human embryonic stem cell; iPSC, induced pluripotent stem cell; VP, venipuncture.