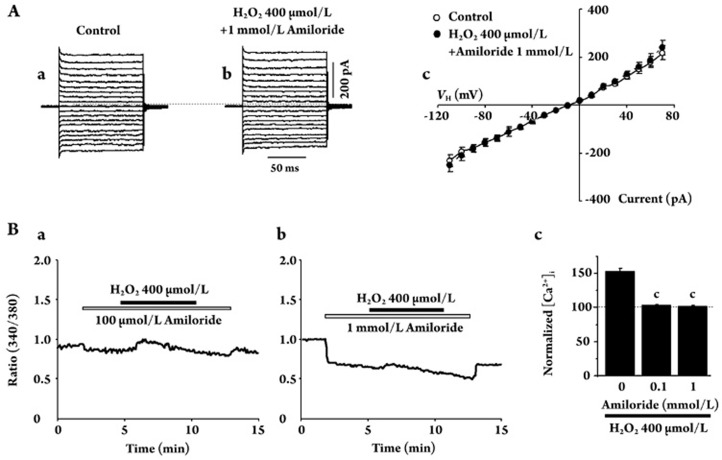
Figure 6.
Effects of amiloride on H2O2-induced changes in membrane conductance and [Ca2+]i. (A) Amphotericin B-perforated whole-cell currents recorded in the presence of 1 mmol/L amiloride before (a) and during (b) application of 400 μmol/L H2O2. Ac: Current-voltage relationships from the data (n=6) shown in (Aa,b) before (○) and during (•) application of H2O2. Ba: [Ca2+]i was measured in the presence of amiloride (100 μmol/L), and then 400 μmol/L H2O2 was applied. Bb: The concentration of amiloride was 1 mmol/L. Bc: Normalized [Ca2+]i from the data of 4−8 experiments shown in (Ba) and (Bb). Application of amiloride by itself caused a decrease in the Fura-2 intensity ratio. The change in the baseline level (Fura-2 intensity ratio) by amiloride seems to be due to some non-specific, direct reversible effect of amiloride on Fura-2 activity because both the appearance and disappearance of the effect are very quick. cP<0.01 vs Amiloride 0 mmol/L.