Figure 8. Vaginal egg injection increases numbers of HIV target cells in the vaginal submucosa.
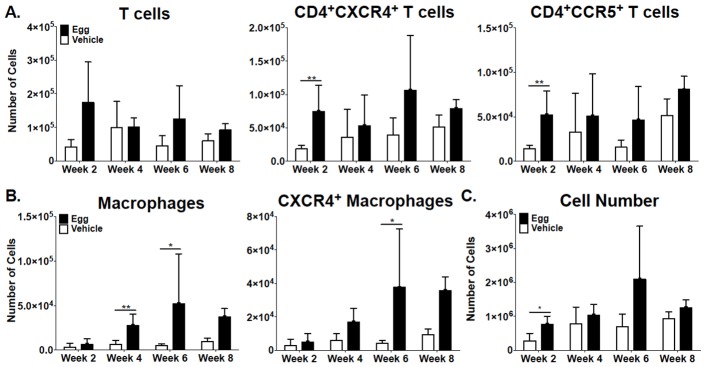
Mice injected with 3000 S. haematobium eggs in the posterior vaginal wall were sacrificed at 2, 4, 6, and 8 weeks post-egg injection (n = 6/group for weeks 2–6 and n = 3/group for week 8). Mice vaginas were isolated and processed for flow cytometric analysis. (A) T-cell subsets were defined by surface expression of CD3, CD4, CD8, CCR5, and CXCR4. Numbers of CD4+ CXCR4+ and CD4+ CCR5+ T cells were significantly increased in egg-injected vaginas at two weeks post-egg injection compared to vehicle-injected controls. (B) Macrophage populations were defined by the surface markers CD11b, F4/80, MerTK, CD64, and CXCR4. Numbers of total macrophages were increased significantly in egg- versus control-injected mice at 4 and 6 weeks post- injection and at 6 weeks for CXCR4+. (C) Cell numbers were counted using a hematocytometer and averaged from two separate counts per sample. Leukocytes were counted while large, morphologically distinct vaginal epithelial cells were excluded. At two weeks, compared to control-injected mice, egg-injected mice exhibited significantly increased numbers of leukocytes in vaginal tissue at 2 weeks post-egg injection.
