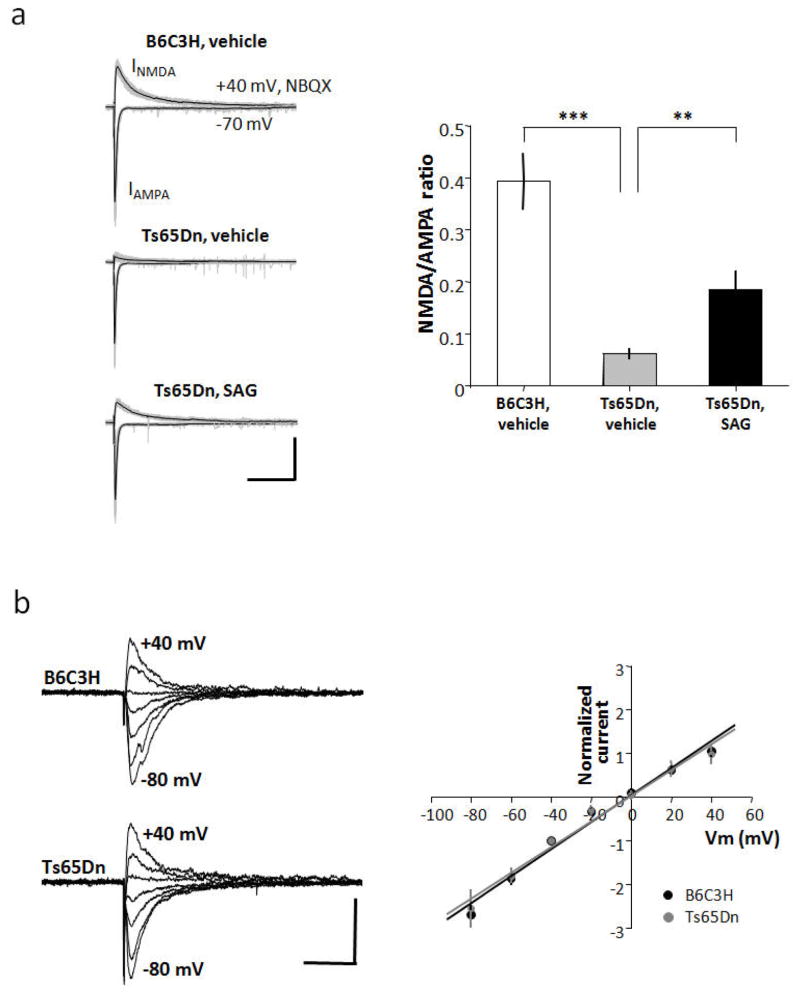
Fig. 5.
SAG partially rescues attenuated NMDA-EPSCs in hippocampal slices from Ts65Dn mice. a) Current-voltage (I–V) relationship in CA1 pyramidal neurons derived from euploid (n=4) and Ts65Dn (n=4) hippocampal slices (10- to 12-week-old male mice). Raw single traces show evoked excitatory post synaptic currents (EPSCs) obtained while holding postsynaptic cells at membrane potentials ranging from −80 mV to +40 mV in 20 mV steps recorded in the presence of D-AP5 (50 μM) and GABAzine (10 μM) to isolate AMPAR-mediated EPSCs. For measurement of I–V curves, spermine (100 μM) was added to block GluR2-lacking AMPARs at positive potentials. Graph shows I–V relationship normalized to the peak EPSC amplitude at −40 mV (Vm indicates membrane potential). The data were fitted by a line giving an estimate for the reversal potential of −0.9 mV (euploid in black) and −0.5 mV (Ts65Dn in gray), respectively (corrected for liquid junction potential). The voltage dependence of the evoked AMPA current was not significantly different between euploid and Ts65Dn. Scale bars: 100 pA, 50 ms. b) Raw (gray) and averaged (black) traces from a series of 20 consecutive evoked EPSCs recorded from hippocampal Schaffer collateral-CA1 synapses (10- to 12-week-old male mice). Peak AMPA currents were measured at −70 mV, and NMDA currents at +40 mV in the presence of NBQX. The NMDA/AMPA ratio was diminished in Ts65Dn neurons (n = 11) compared with euploid (n = 13). SAG treatment significantly increased NMDA currents in Ts65Dn neurons (n=11). Error bars represent the mean ± SEM. (TsVeh vs. TsSAG, p=0.003; EuVeh vs. TsVeh p=1.7E-5; EuVeh vs. TsSAG, p=0.006, unpaired two-tailed Student’s t test). Scale bars: 200 pA, 250 ms.