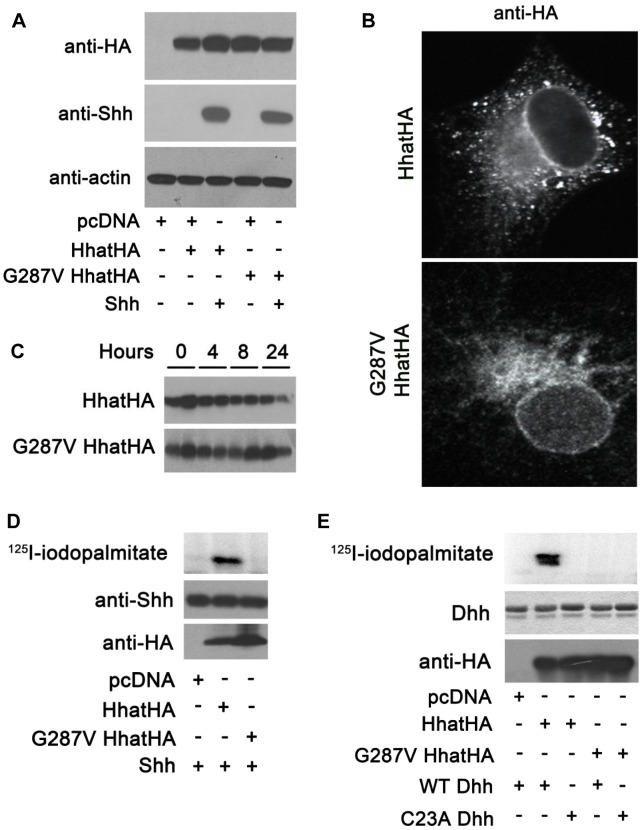
Figure 3. G287V mutation results in loss of HHAT activity.
A) COS-1 cells were transfected with the indicated constructs and cell lysates were analyzed directly by Western blotting. B) COS-1 cells transfected with wild type or G287V HHAT-HA were fixed and processed for indirect immunofluoresence and stained with the antibodies indicated. C) COS-1 cells were transfected with the indicated HHAT construct and incubated in DMEM supplemented with 10% FBS, 100 µg/ml cyclohexamide, and 40 µg/ml chloramphenicol. At each indicated time point, cells were lysed and subjected to SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with anti-HA antibodies. The amount of HA signal at each time point was determined using GS-800 Calibrated Densitometer (BioRad). Experiments were carried out in duplicate and repeated three times. D) In vitro palmitoylation assay using SHH and membranes from cells expressing wild type or G287V HHAT. Top panel, incorporation of 125I-iodopalmitate into SHH detected by phosphorimaging. Middle panel, Anti-SHH Western blot. Lower panel, Anti-HA Western blot. Experiments were carried out in duplicate and repeated three times. E) In vitro palmitoylation assay using DHH and membranes from cells expressing wild type or G287V HHAT. Top panel, incorporation of 125I-iodopalmitate into DHH detected by phosphorimaging. Middle panel, Coomassie-staining of DHH. Lower panel, Anti-HA Western blot. Experiments were carried out in duplicate and repeated three times.