Fig. 7.
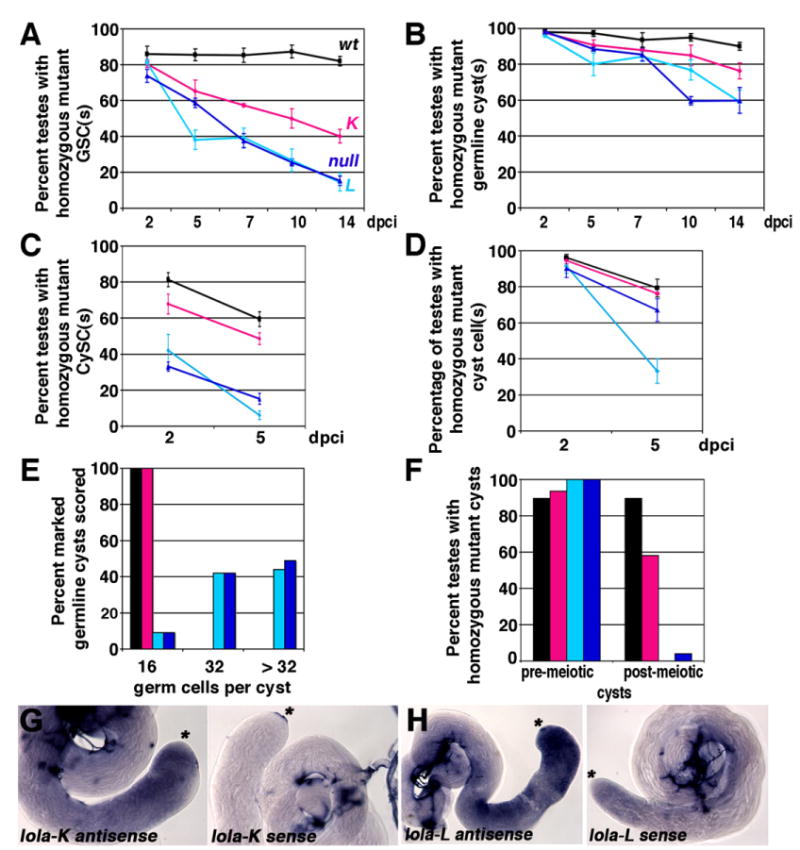
Requirements for lola-K and lola-L differ in the testis: (A) and (B) Percentage of mosaic testes containing homozygous mutant or marked control (A) GSCs or (B) spermatogonial and/or spermatocyte cyst(s) from 2 to 14 dpci. (C) and (D) Percentage of mosaic testes containing homozygous mutant or marked control (C) CySC(s) or (D) cyst cell(s) from 2 to 5 dpci. (E) Percentage of homozygous mutant or marked control or germline cysts in the spermatocyte region with 16, 32, or greater than 32 germ cells per cyst. n=100 cysts scored per genotype at 4–6 dpci. (F) Percentage of mosaic testes containing homozygous mutant or marked control cyst(s) in the spermatocyte region or post-meiotic spermatid cyst(s) at 4–6 dpci. (A)–(F): Black: FRT42D wildtype control clones. Magenta: lolaORC4 (K-specific) clones. Turquoise: lolaORE119 (L-specific) clones. Blue: lolaORE76 (null) clones. (G) and (H) In situ hybridization on wildtype testes with riboprobes complementary to the (G) lola-K specific exons and (H) lola-L specific exon. Left: Anti-sense probe. Right: Sense probe. Asterisks: Apical tip. Stained structures in sense testes are trachea.
