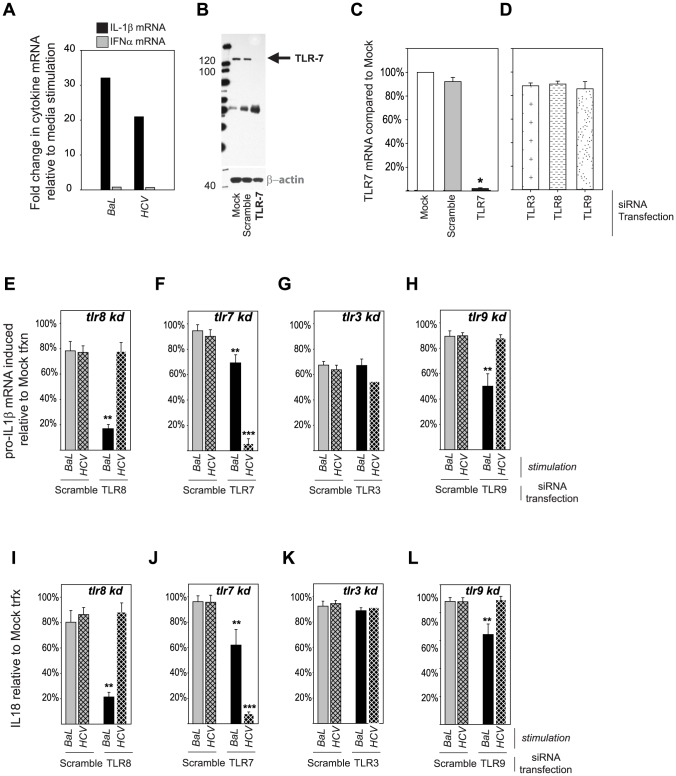
Figure 4. Differential importance of endosomal TLRs in inflammasome sensing of HIV and HCV.
Monocytes were cultured without stimulation or with HIVBaL or HCVSubject 180 and IL-1β, IFNα and measured at multiple timepoints. Fold change in expression of IL-1β (black bar) and IFNα (grey bar) following HIVBaL or HCVSubject 180 relative to stimulation with media alone is shown at 6 h (A). Functional knockdowns of the endosomal located TLRs in monocytes were generated by RNA interference. Monocytes were mock transfected or transfected with either siRNA targeting TLR7 or a non-targeting sequence (Scramble). After 24 h, cell lysates were prepared and efficacy of knockdown determined by (B) western blot and (C) qRT-PCR. (D) Specificity of the TLR7 siRNA was confirmed by qRT-PCR using primers for TLR3, TLR7, TLR8, and TLR9. (*) denotes comparisons with p≤0.05 compared to the mock transfected cells. Monocytes in which endosomal TLR knockdown were generated were cultured with HIVBaL (solid bars) or HCVSubject 180 (hatched bars) and pro-IL-1β mRNA transcription measured at 6 h (E–H) and IL-18 secretion measured at 24 h (I–L). Shown are the relative production of pro-IL-1β mRNA and IL-18 in TLR8 (E, I), TLR7 (F, J), TLR3 (G, K) and TLR9 (H, L) knockdown monocytes normalized to mock transfected monocytes (no siRNA) stimulated with the same viruses. Bars represent the mean ± S.D. for n = 6–9 independent transfection experiments, (**) denotes comparisons with p≤0.05 and (***) denoted p≤0.001 compared to the scramble siRNA transfected cells.