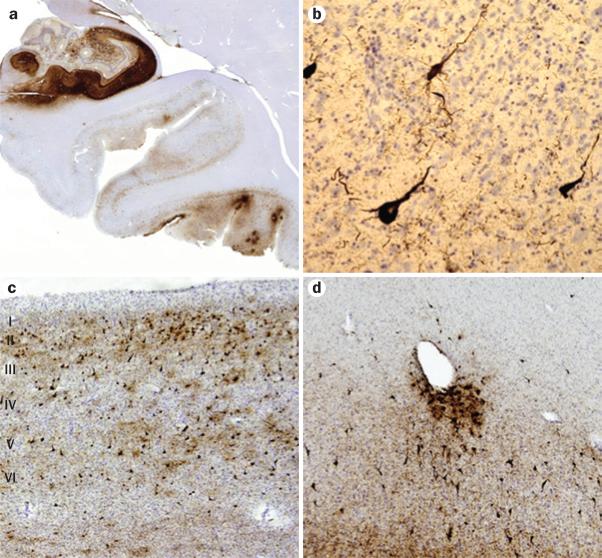
Figure 3.
Histopathological features of chronic traumatic encephalopathy in a former professional football player. All sections are immunostained for abnormally phosphorylated tau using an AT-8 monoclonal antibody that detects hyperphosphorylated tau (Ser202 and Thr205). a | Scanning view of the hippocampus and parahippocampal cortex. Note intense immunostaining of the entire Ammon horn and subiculum, with focal involvement at the depths of sulci of the inferior temporal lobe. Original magnification ×1. b | Appearance of individual neurofibrillary tangles in the neocortex. Original magnification ×160. c | Neurofibrillary tangles in the anterior insular cortex form preferentially in the superficial layers (layers II–III), rather than in deeper layers (layers V–VI) as is more common in Alzheimer disease. Original magnification ×30. d | Tendency for perivascular tau deposition and neurofibrillary tangle formation in the frontal cortex. Original magnification ×60. Permission obtained from the American Medical Association © Shively, S. et al. Arch. Neurol. 69, 1245–1251 (2012).