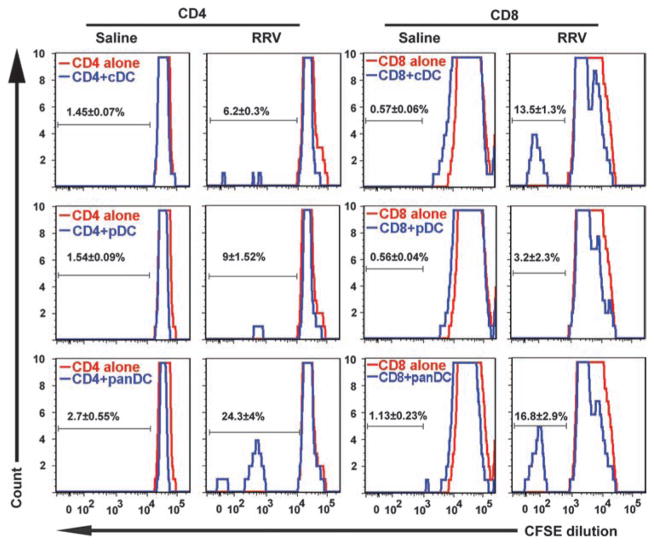
Fig. 4.
Neonatal T lymphocyte proliferation induced by pDCs, cDCs, and panDCs. Hepatic CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes were isolated from 3-day-old control mice or 3 days after injection of newborn mice with RRV or saline. Proliferation of hepatic CD4+ and CD8+ T lymphocytes was measured by flow cytometry after 48 hours of culture with hepatic cDCs, pDCs, or panDCs (pDCs + cDCs). DCs from saline-injected mice did not induce proliferation of CD4+ or CD8+ T cells (measured by dilution of CFSE, a fluorescent cell-staining dye). Proliferation increased when RRV-primed cDCs were cocultured with CD8+ T cells, or when CD4+ or CD8+ T cells were cocultured with RRV-primed panDCs. Twenty thousand (7AAD− gated) cells were used for flow cytometry analysis; values within each histogram indicate mean percent ± SD of proliferating T cells from three similar experiments.