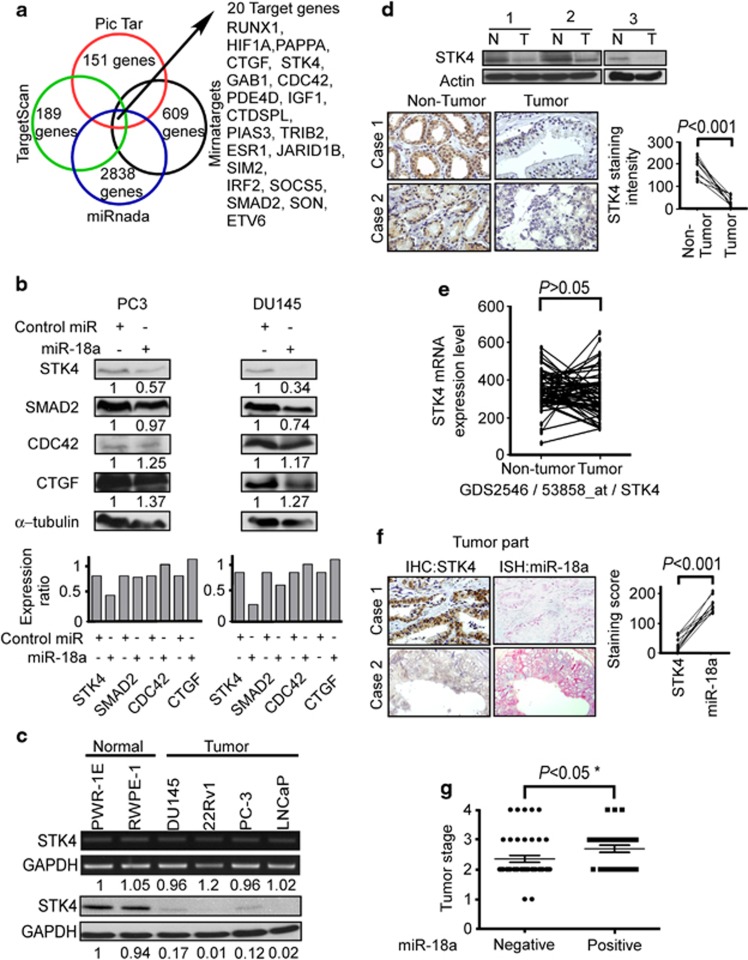
Figure 2.
STK4 is inversely correlated with miR-18a. (a) Venn diagram displaying miRNAs computationally predicted to target STK4 by PicTar (red), TargetScan (green), miRanda (blue) and Mirnatargets (black). Examination of different databases to find candidate downstream target genes. (b) Protein expression of STK4, SMAD2, CDC42, CTGF and α-tubulin in control miR or miR-18a precursor transfected prostate cancer cells (PC-3, DU145). STK4 was suppressed by miR-18a transfection at the protein level in prostate cancer cell lines as shown by western blotting. (c) The expression of STK4 mRNA (upper panel) and protein (bottom panel) in six prostate cell lines was analyzed by RT-PCR and western blotting, respectively. The number below the GAPDH image was the density ratio of STK4/GAPDH (NIH-Image J) for mRNA (upper panel) and protein (bottom panel), respectively. The STK4 mRNA level was the same in 60 cell lines. The STK4 protein level is downregulated in four prostate cancer cell lines. (d) Western blotting (upper panel) and IHC (middle panel) analysis revealed STK4 protein level was downregulated in prostate tumor parts compared with adjacent non-tumor tissues. Quantification of STK4 expression in paired prostate adenocarcinoma and corresponding normal tissues (bottom panel) (n=10, P<0.001). Western blotting data showed that the STK4 protein is highly expressed in non-tumor compared with tumor tissues. IHC showed that STK4 staining is lost in the tumor tissues. (e) STK4 mRNA expression levels are not different between normal and tumor of prostate cancer in GEO data set validation. (f) ISH and IHC were used to detect the presence of miR-18a and STK4 in prostate cancer tissues. These sections of ISH and for IHC are consecutive sections. Quantitative IHC and ISH scores show that STK4 and miR-18a expression are inversely correlated. (g) miR-18a is highly expressed with poor tumor stage.