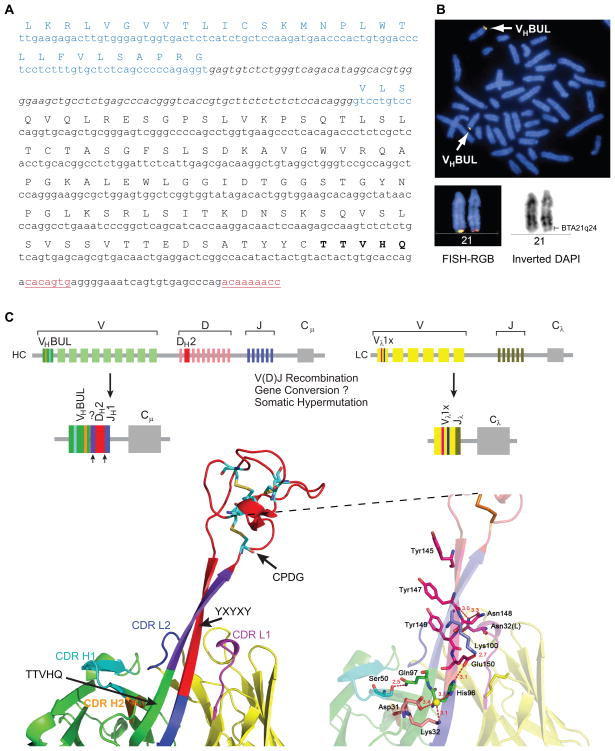
Figure 3. Genetic basis for ultralong antibody formation.
(A) Identification of VHBUL, a germline variable region used in ultralong antibodies. The leader sequence is in blue, coding sequence is indicated with the amino acid translation above, the intron is in italics, and the unique TTVHQ extension, which forms a portion of the ascending strand of the stalk is in bold. The recombination signal sequence heptamer and nonamer are underlined in red. (B) The VHBUL region is found on chromosome 21. Partial cattle metaphase spread (left) and enlarged chromosome 21 (top right) showing the location of VHBUL region in BTA21q24 by two-color FISH with BAC clones 318H2 (green) and 14-74H6 (red). International nomenclature for BTA21 is depicted at the bottom. (C) Schematic of the bovine immunoglobulin loci depicting VHBUL, DH2, and Vλ1x, which are preferentially used in ultralong antibodies. The process of V(D)J recombination assembles the gene segments to form functional ultralong heavy and light chain genes. (bottom left) The V-D-J regions mapped onto the BLV1H12 Fab structure. Colors of the gene segments correlate with the colors of the structure. VHBUL is unique in encoding CDR H1 and CDR H2 residues that interact with the stalk (cyan and orange), as well as a TTVHQ motif that initiates the ascending β-strand. Similarly, the Vλ1x light chain encodes CDR L1 and CDR L2 residues that interact with the stalk (magenta and blue). Arrows indicate areas of potential junctional diversity. Relatively long V-D insertions are indicated in purple. It is unclear whether this sequence results from N-additions, gene conversion, or another mechanism. (bottom right) A detailed depiction of the interactions of CDR H1, H2, L1, and L2 with the stalk of BLV1H12, as well as the location of the YxYxY motif of the descending strand. See also Table S4.