Figure 1.
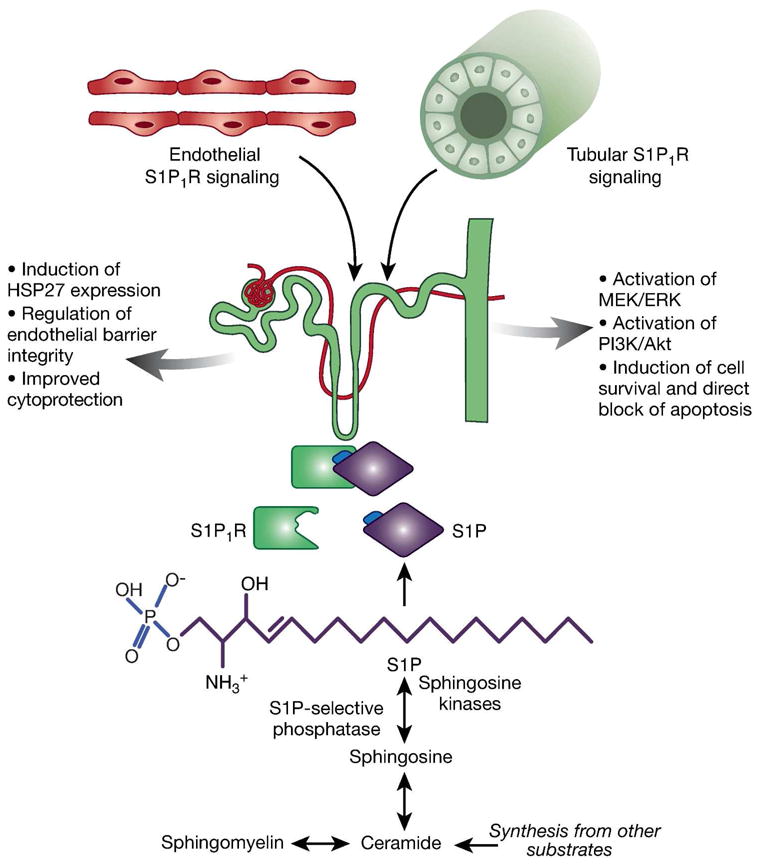
Effects of vascular endothelial and tubular sphingosine-1-phosphate receptor (S1P1R) signaling in ischemic Acute Kidney Injury (AKI). Sphingosine-1-phosphate (S1P) is synthesized from the sphingolipids sphingosine, sphingomyelin, ceramide, and others. S1P synthesis is dependent on the activity of sphingosine kinases and S1P-selective phosphorylase, as they regulate phophorylation of sphingosine to S1P (marked with blue font in figure). As a ligand for S1P1R, S1P initiates various signaling pathways. Endothelial-specific S1P1R deletion is associated with increased renal tubular necrosis, inflammation, impaired vascular permeability and exacerbates renal tubular apoptosis after ischemic AKI. One mechanism for the protective effects of endothelial S1P1R activation lies within the induction of heat-shock protein (HSP)273. In proximal tubule, S1P1R activation leads to direct blockage of apoptosis and induction of cell survival via activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular regulated kinase (MEK/ERK) and phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt induced pathways9.
