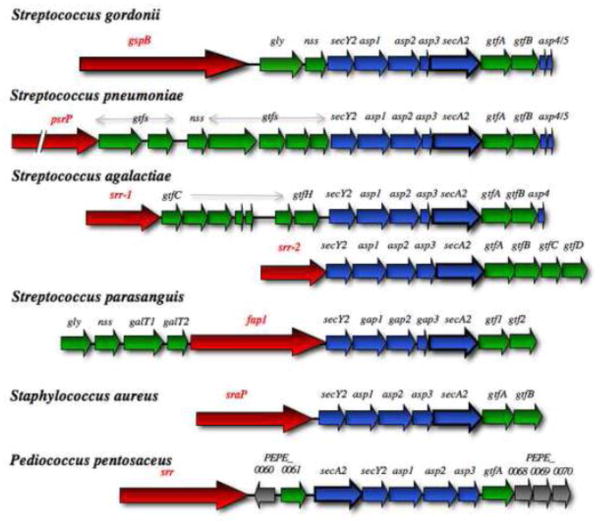
Figure 4. Gene organization within the accessory Sec loci.
Comparison of the aSec locus in selected Gram-positive bacterial species. Genes encoding the aSec system components are colored blue, and the export susbstrate is shown in red. Glycosyl transferases and other enzymes involved solely in carbohydrate modifications are shown in green. Genes of unknown function are shown in grey, while genes encoding potential regulatory proteins are depicted in black. Two different variations found in Streptococcus agalactiae strains are shown. The Staphylococcus locus is representative of most Staphylococcal species. A slightly different arrangement, in which secA2 is immediately upstream of secY2 and the asp123 genes, is found in Pediococcus, Enterococcus and some Lactobacillus species.