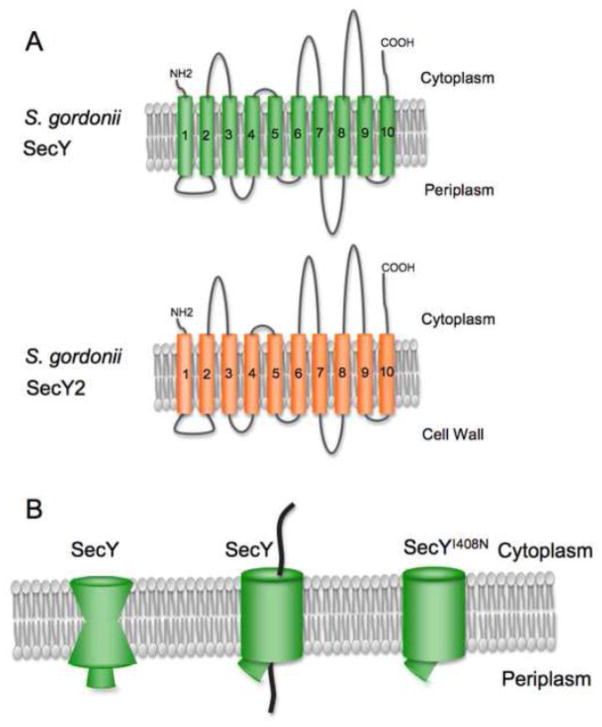
Figure 7. SecY versus SecY2 topology and structural features.
A: The predicted topology of SecY2 is very similar to that of SecY. B: The inactive SecY channel is impermeable to small molecules, due to the constriction by a ring of hydrophobic residues near the center of the channel along with a plug formed by residues of TM2. In the active channel, the central pore widens and the plug is displaced. Some prl mutations in E. coli SecY result in a partially or more readily opened channel.