FIGURE 6.
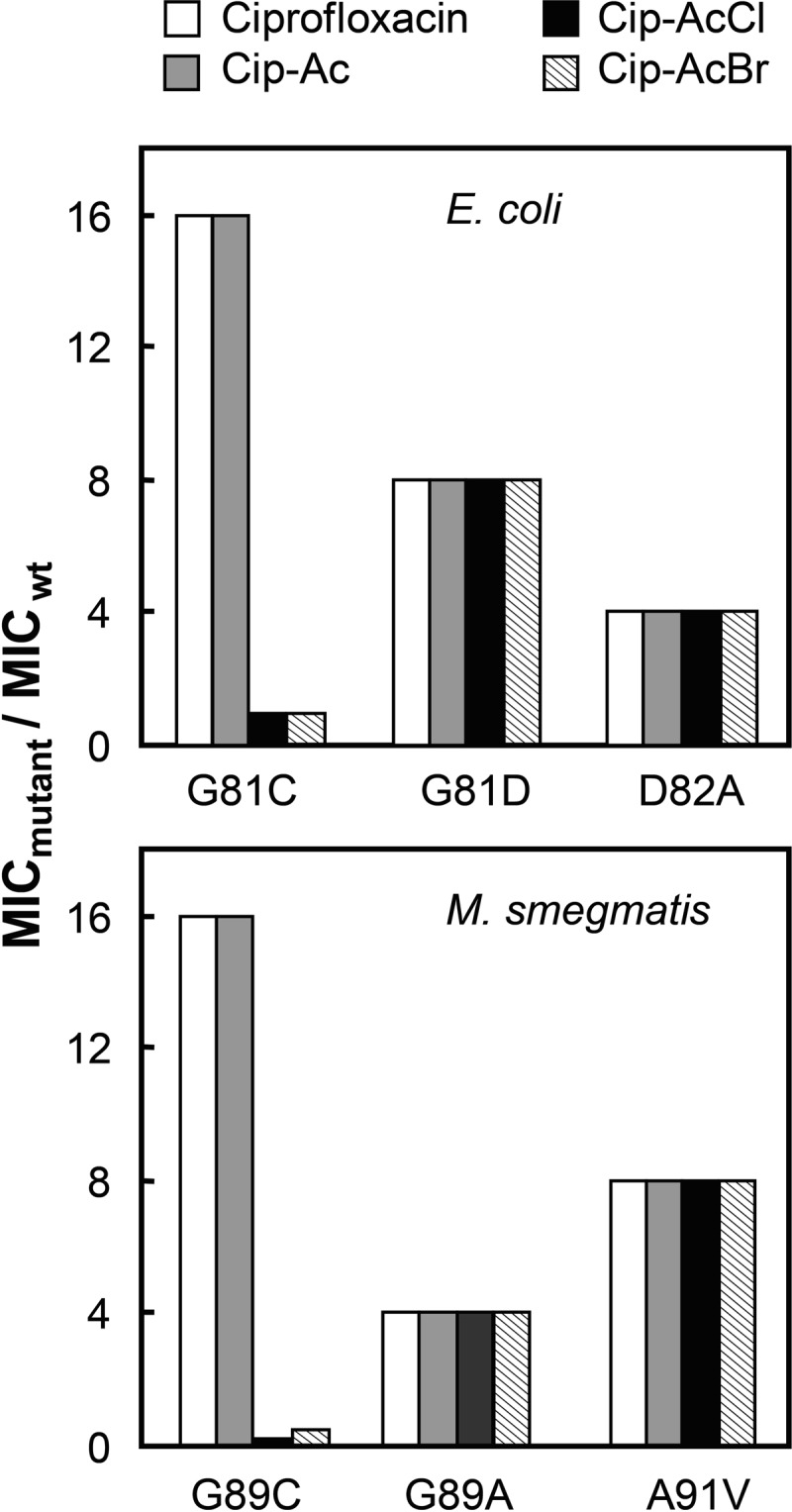
Effect of chloroacetyl and bromoacetyl substituents attached to ciprofloxacin on growth inhibition of GyrA Cys variants. The MIC was determined with the indicated mutants for ciprofloxacin derivatives (white bars, ciprofloxacin; gray bars, Cip-Ac; black bars, Cip-AcCl; striped bars, Cip-AcBr) with E. coli (upper panel) and M. smegmatis (lower panel). Data are expressed as multiples of values for MIC determined with wild-type E. coli strain DM4100 (MIC = 0.01 μg/ml for ciprofloxacin, 0.3 μg/ml for Cip-Ac, 0.25 μg/ml for Cip-AcCl, and 0.5 μg/ml for Cip-AcBr) or wild-type M. smegmatis strain mc2155 (0.1 μg/ml for ciprofloxacin, 0.16 μg/ml for Cip-Ac, 0.5 μg/ml for Cip-AcCl, and 0.5 μg/ml for Cip-AcBr). For strain numbers, see Table 1. Three independent experiments gave identical results, precluding determination of error bars.
